Grocery store insurance costs average $87-95 monthly for comprehensive business owner’s policies, yet with 84.41% of property and casualty insurance companies reporting $974,969,511,332 in direct premiums written across all commercial lines, many retailers remain underinsured against critical risks. Independent grocers face unique exposures including customer slip-and-fall incidents, product contamination claims, and employee workplace injuries that can devastate finances without proper grocery store insurance protection.
Modern grocery operations encounter escalating risks from cyber threats targeting payment systems, supply chain disruptions affecting perishable inventory, and evolving premises liability standards that hold retailers accountable for customer safety. Comprehensive grocery store insurance programs address these evolving risks through specialized coverage designed for food retail operations. Commercial lines recorded premium growth with average increases of 5.2% across all account sizes in Q2 2024, reflecting insurers’ recognition of heightened risk exposure in retail environments requiring comprehensive grocery store insurance strategies.
Understanding grocery store insurance requirements becomes essential as regulatory compliance demands intensify and litigation costs continue rising. Professional business insurance compliance requirements establish the foundation for protecting retail operations while meeting state-mandated coverage levels for workers compensation and general liability exposures.
This comprehensive analysis examines current grocery store insurance costs, mandatory coverage types, regulatory requirements, and strategic risk management approaches that help independent retailers protect their business assets while maintaining operational efficiency throughout 2025.
On This Page
Essential Overview
“Grocery retailers require multi-layered insurance protection covering customer liability, employee injuries, property damage, cyber threats, and business interruption risks, with Business Owner’s Policies typically providing cost-effective bundled coverage starting around $87-95 monthly for comprehensive protection.”
What Kind of Grocery Store Insurance Do I Need for a Retail Store?

Retail grocery stores require several essential grocery store insurance coverages to protect against the diverse risks inherent in food retail operations. General liability insurance serves as the foundation of any grocery store insurance program, protecting against customer injuries from slip-and-fall accidents, foodborne illness claims, and property damage incidents occurring on store premises.
Commercial property insurance protects the physical assets of grocery stores, including buildings, refrigeration equipment, inventory, and point-of-sale systems. This coverage becomes particularly critical for stores with significant investments in specialized equipment like walk-in coolers, freezers, and deli preparation areas that require expensive repairs or replacement.
Effective grocery store insurance programs combine general liability with property coverage through Business Owner’s Policies. Grocery stores pay an average of $87 per month, or $1,042 per year, for a business owner’s policy that bundles general liability with commercial property protection. This Business Owner’s Policy (BOP) approach typically costs less than purchasing separate policies while providing comprehensive grocery store insurance coverage for most standard retail risks.
PRO TIP: Business Owner’s Policies often include business interruption coverage, which pays for lost income and operating expenses if covered damage forces temporary closure for repairs.
Workers’ compensation insurance is legally required in most states for grocery stores with employees. This coverage pays medical expenses and wage replacement for employees injured while performing job duties, from lifting heavy shipments to operating food preparation equipment.
| Essential Coverage Types | Average Monthly Cost | Primary Protection |
|---|---|---|
| Business Owner’s Policy | $87-95 | Liability + Property |
| Workers’ Compensation | $80-123 | Employee Injuries |
| Commercial Auto | $171 | Vehicle Accidents |
| Cyber Liability | $57 | Data Breaches |
Product liability insurance protects grocery stores against claims alleging that sold products caused illness or injury to customers. While manufacturers typically carry primary product liability coverage, retailers can face lawsuits claiming improper storage, handling, or sale of contaminated or expired products.
Cyber liability insurance has become increasingly important as grocery stores process credit card transactions and maintain customer databases. Grocery stores and other retail business owners pay an average of $57 per month, or $683 annually, for cyber insurance protecting against data breaches, payment system hacks, and business interruption from cyber attacks. Advanced grocery store insurance portfolios include comprehensive cyber protection.
Stores selling alcoholic beverages need liquor liability insurance to protect against claims involving customers who consume alcohol purchased at the store and subsequently cause injury or property damage. Many states require this coverage for retailers with liquor licenses as part of comprehensive grocery store insurance compliance.
IMPORTANT NOTE: Coverage requirements vary significantly by state, store size, and specific operations. Stores with prepared food sections, pharmacies, or gas stations require additional specialized coverage within their grocery store insurance programs.
The professional liability insurance protection framework applies to grocery stores offering specialized services like pharmacy operations, nutritional consulting, or custom catering that involve professional advice or specialized expertise requiring enhanced grocery store insurance coverage.
What is Grocery Store Insurance?
Grocery store insurance encompasses specialized commercial insurance policies designed specifically for food retail operations, addressing the unique risks that grocery stores face in their daily operations. Unlike general retail insurance, grocery store insurance accounts for specific exposures related to perishable inventory, food safety regulations, and customer interaction with potentially hazardous products.
The foundation of effective grocery store insurance lies in understanding the multi-faceted nature of food retail risks. The average supermarket & grocery store insurance cost is $90 per month or $1,080 per year for a $1 million general liability insurance, but comprehensive grocery store insurance protection requires multiple coverage layers addressing property, liability, and operational risks.
Spoilage coverage represents a critical component unique to grocery store insurance programs, protecting against financial losses when perishable inventory becomes unsaleable due to equipment failure, power outages, or temperature fluctuations. This coverage can prevent devastating financial losses when refrigeration systems fail, potentially destroying thousands of dollars in frozen and refrigerated products.
Equipment breakdown insurance specifically addresses the specialized machinery essential to grocery operations, including commercial refrigeration units, freezers, generators, and food processing equipment. When these systems fail, repair costs can quickly exceed tens of thousands of dollars while business interruption losses compound during extended downtime. Professional grocery store insurance programs address these equipment-specific risks.
| Grocery-Specific Coverage | Monthly Cost Range | Coverage Focus |
|---|---|---|
| Spoilage Protection | $25-45 | Perishable Inventory |
| Equipment Breakdown | $30-60 | Refrigeration/HVAC |
| Food Contamination | $20-40 | Product Recall |
| Liquor Liability | $28-35 | Alcohol Sales |
Food contamination coverage protects against claims arising from contaminated products sold to customers, even when contamination occurs at the supplier level. This coverage can include costs for product recalls, customer notification, and business interruption during contamination investigations. Comprehensive grocery store insurance programs include robust food contamination protection.
Business interruption insurance for grocery stores often includes extended coverage for utility interruptions, recognizing that power outages can force closures and result in complete inventory losses for stores heavily dependent on refrigeration. Advanced grocery store insurance policies provide comprehensive business interruption protection.
WARNING: Standard business interruption policies may not cover losses from utility company failures or civil authority orders unless specifically included in grocery store insurance policies.
The federal government requires every business with employees to have workers’ compensation coverage, which becomes particularly complex for grocery stores due to varying risk levels across different job functions, from cashiers to butchers to stock personnel handling heavy merchandise. Effective grocery store insurance programs ensure full workers’ compensation compliance.
Employment practices liability insurance (EPLI) addresses the grocery industry’s exposure to workplace harassment, discrimination, and wrongful termination claims, which can arise in retail environments with diverse workforces and customer interaction pressures. Modern grocery store insurance portfolios include comprehensive EPLI protection.
The complete workers comp requirements by state provide essential guidance for grocery store owners navigating varying state mandates for employee injury protection within their grocery store insurance programs.
IMPORTANT NOTE: Many grocery store insurance policies include automatic coverage extensions for seasonal employees and temporary workers during peak periods like holidays.
How Much is Grocery Store Insurance for a Convenience Store?
Convenience stores, which often overlap with small grocery operations, face similar but distinct grocery store insurance cost structures compared to larger grocery retailers. General liability insurance costs 61% of our customers $74 on average per month for convenience store operations, reflecting the higher customer traffic volume and extended operating hours typical of these businesses.
The fundamental difference in convenience store grocery store insurance costs stems from operational risk factors including extended hours, cash-intensive transactions, and higher crime exposure due to late-night operations. These factors typically increase premiums by 15-25% compared to traditional daytime-only grocery operations requiring standard grocery store insurance coverage.
Workers’ compensation costs for convenience stores vary significantly based on employee duties and hours worked. Workers’ compensation insurance median cost is $123 per month for convenience store operations, with higher rates reflecting increased injury risks from handling cash, cleaning chemicals, and working alone during overnight shifts. Comprehensive grocery store insurance programs address these elevated workers’ compensation exposures.
Commercial property insurance for convenience stores must account for higher theft and vandalism risks, particularly for locations in urban areas or those operating 24/7. Coverage typically costs $33-68 monthly but may increase substantially based on crime statistics for specific locations requiring enhanced grocery store insurance protection.
| Convenience Store Coverage | Monthly Range | Risk Factors |
|---|---|---|
| General Liability | $74-95 | Customer Volume |
| Workers’ Compensation | $123-150 | Shift Work/Cash Handling |
| Commercial Property | $33-68 | Theft/Vandalism |
| Crime/Theft Coverage | $45-75 | Cash on Premises |
Crime insurance becomes essential for convenience stores due to cash-intensive operations and extended hours increasing robbery risks. This coverage protects against employee theft, customer robbery, and electronic payment system fraud, with costs typically ranging from $45-75 monthly depending on security measures and location. Professional grocery store insurance programs include comprehensive crime protection.
Cyber liability coverage costs approximately $57 monthly for convenience stores, addressing payment card industry (PCI) compliance requirements and protecting against data breaches affecting customer credit card information stored in point-of-sale systems. Modern grocery store insurance portfolios incorporate robust cyber liability protection.
Liquor liability insurance represents a significant cost component for convenience stores selling alcoholic beverages, with monthly premiums ranging from $28-50 depending on alcohol sales volume and local regulations governing off-premise consumption. Comprehensive grocery store insurance programs ensure full liquor liability compliance.
PRO TIP: Many convenience stores can reduce grocery store insurance costs by implementing security measures like surveillance cameras, drop safes, and improved lighting, which may qualify for premium discounts.
Commercial auto liability and physical damage were the commercial lines with the highest percentage growth at 12.2% and 14.9%, respectively, affecting convenience stores using delivery vehicles or company cars for business operations requiring commercial auto coverage within their grocery store insurance programs.
The escalating costs reflect increased accident settlements and vehicle repair expenses, making it crucial for convenience store owners to evaluate their commercial auto coverage limits and deductibles annually as part of comprehensive grocery store insurance planning.
How Much is Retail Grocery Store Insurance?
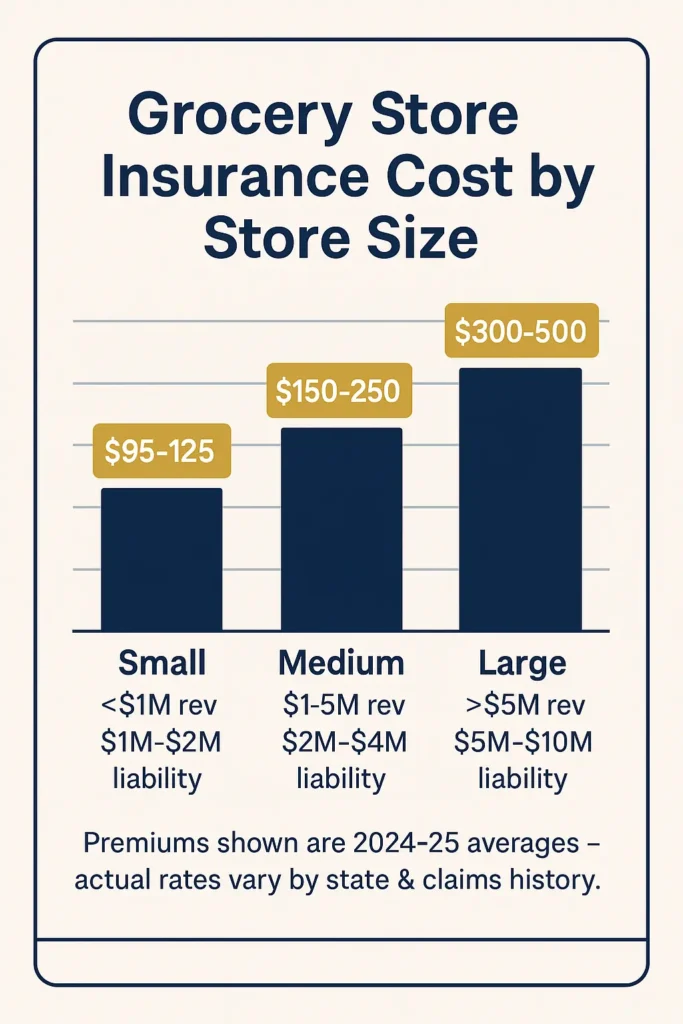
Retail grocery store insurance costs for grocery and food retail operations vary significantly based on store size, location, inventory value, and specific risk exposures. Retail businesses pay an average of $95 per month, or $1,136 per year, for a business owner’s policy that bundles essential coverage types into cost-effective packages.
Understanding the factors driving retail grocery store insurance costs helps grocery store owners budget appropriately and identify potential savings opportunities. Store size measured by square footage, annual revenue, and number of employees represents the primary cost determinant, with larger operations facing proportionally higher premiums due to increased exposure.
Location risk factors significantly impact retail grocery store insurance costs, with stores in high-crime areas, flood zones, or regions prone to natural disasters paying substantially higher premiums. Urban locations typically pay 20-40% more than suburban stores due to increased theft, vandalism, and liability exposures.
Inventory characteristics affect property insurance costs, with grocery stores paying higher rates than general retailers due to perishable inventory requiring specialized storage and handling. High-value inventory, including premium wines, organic products, and prepared foods, increases property coverage needs and associated grocery store insurance costs.
| Store Size Category | Annual Revenue | Average Monthly Premium | Coverage Limits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Small Grocery | Under $1M | $95-125 | $1M/$2M Liability |
| Medium Grocery | $1M-$5M | $150-250 | $2M/$4M Liability |
| Large Grocery | Over $5M | $300-500 | $5M/$10M Liability |
Claims history represents a critical factor in retail grocery store insurance pricing, with stores having previous liability or property claims potentially facing 25-50% higher premiums. Conversely, claim-free operations may qualify for significant discounts and favorable renewal terms.
Risk management programs can substantially reduce retail grocery store insurance costs through implementation of safety protocols, employee training, and loss prevention measures. Many insurers offer premium credits for certified safety programs, security system installations, and regular safety audits..
In 2024, the median monthly cost of a business insurance policy for new Progressive customers ranged from $42 for professional liability to $80 for workers’ compensation, demonstrating the wide range of coverage costs based on specific policy types and risk characteristics.
Commercial umbrella insurance provides additional liability protection beyond standard policy limits, with retailers paying an average of $59 per month, or $707 annually, for commercial umbrella insurance available in $1 million increments for enhanced protection against catastrophic claims.
IMPORTANT NOTE: Many landlords require retail tenants to carry liability insurance with limits exceeding $2 million, making umbrella coverage necessary to meet lease requirements for comprehensive grocery store insurance protection.
The cyber insurance for business protection has become increasingly critical for retail operations processing electronic payments and maintaining customer databases, with costs typically ranging from $50-100 monthly based on data exposure levels requiring specialized grocery store insurance coverage.
What Grocery Store Insurance Do I Need to Run a Shop?

Operating a retail grocery shop requires multiple grocery store insurance policies to protect against the diverse risks inherent in food retail operations. General liability insurance serves as the mandatory foundation, providing protection against customer injuries, property damage claims, and advertising injury lawsuits that can arise in retail environments.
Commercial property insurance protects the physical assets essential to shop operations, including buildings, inventory, equipment, and fixtures. For grocery shops, this coverage must account for specialized equipment like refrigeration units, deli slicers, and point-of-sale systems that require expensive repairs or replacement when damaged.
Workers’ compensation insurance is legally required in virtually all states for shops with employees, covering medical expenses and wage replacement for work-related injuries. Workers’ compensation insurance protects not just your employees but also your business from financial losses if one of your workers ever gets sick or injured on the job, making it essential for compliance and financial protection within comprehensive grocery store insurance programs.
Business interruption insurance protects against income losses when covered events force temporary closure or reduce operations. For grocery shops dependent on perishable inventory, this coverage often includes utility interruption protection and extra expense coverage for alternative operating locations as part of complete grocery store insurance portfolios.
| Mandatory Coverage | Legal Requirement | Primary Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Workers’ Compensation | Required if employees | Employee injury protection |
| General Liability | Often required by lease | Third-party injury/damage |
| Commercial Auto | Required for business vehicles | Vehicle accident protection |
| Professional Liability | Required for specialized services | Professional error protection |
Commercial auto insurance becomes necessary when shops operate delivery vehicles or use personal vehicles for business purposes. Most states require this coverage for vehicles owned by a grocery store, with coverage extending to property damage, medical costs, and legal expenses from vehicle accidents.
Cyber liability insurance addresses the growing threat of data breaches and cyber attacks targeting retail point-of-sale systems and customer databases. With grocery shops increasingly dependent on electronic payment processing, this coverage protects against financial losses from compromised customer data requiring specialized grocery store insurance protection.
Product liability insurance protects grocery shops against claims alleging that sold products caused illness or injury to customers. While often included in general liability policies, shops selling prepared foods or operating delis may need enhanced product liability coverage within their grocery store insurance programs.
Crime insurance provides protection against employee theft, customer shoplifting, and robbery incidents that can significantly impact grocery shop profitability. This coverage becomes particularly important for cash-intensive operations and shops in high-crime areas requiring comprehensive grocery store insurance protection.
PRO TIP: Many insurance carriers offer package policies combining multiple coverage types at discounted rates compared to purchasing individual policies.
Some states also require additional insurance. Laws requiring insurance vary by state, making it essential for shop owners to research specific state requirements and consult with licensed insurance professionals familiar with local regulations affecting their grocery store insurance obligations.
The commercial dump truck insurance framework applies to grocery shops operating delivery trucks or specialized vehicles for inventory transport and customer service as part of comprehensive grocery store insurance coverage.
IMPORTANT NOTE: Shops selling alcoholic beverages require liquor liability insurance in addition to standard coverage, with specific requirements varying by state licensing regulations that must be incorporated into grocery store insurance programs.
Do Grocery Stores Offer Health Insurance?
Grocery stores as employers face complex decisions regarding health insurance benefits for their workforce, influenced by federal requirements, competitive pressures, and operational costs. Large grocery chains typically offer comprehensive health benefits to attract and retain qualified employees, while independent stores face greater challenges providing affordable coverage due to smaller risk pools and limited resources.
Federal regulations under the Affordable Care Act (ACA) require employers with 50 or more full-time equivalent employees to provide health insurance meeting minimum essential coverage standards or face financial penalties. This mandate significantly impacts larger grocery operations and regional chains operating multiple locations.
Small grocery stores with fewer than 50 employees are not required to provide health insurance but may choose to offer coverage as a competitive advantage in attracting quality workers. Workers’ compensation insurance (sometimes called workman’s compensation insurance or, often, just workers’ comp) protects not just your employees but also your business, but does not replace the need for health insurance benefits.
Health insurance costs for grocery store employers vary significantly based on plan design, employee demographics, and geographic location. Small group health insurance premiums typically range from $400-800 monthly per employee for employer-sponsored coverage, creating substantial financial commitments for grocery store owners.
| Store Size | Health Insurance Obligation | Typical Approach |
|---|---|---|
| Under 50 employees | No mandate | Optional benefit |
| 50+ employees | ACA mandate | Required coverage |
| Union workforce | Collective bargaining | Negotiated benefits |
| Part-time heavy | Reduced obligation | Limited coverage |
Alternative benefits strategies allow smaller grocery stores to provide health-related benefits without traditional insurance costs. Health Savings Accounts (HSAs), direct primary care arrangements, and health reimbursement arrangements (HRAs) offer flexible options for supporting employee healthcare needs.
Union considerations significantly impact health insurance decisions for grocery stores with unionized workforces. Collective bargaining agreements often specify health insurance requirements, contribution levels, and plan features that employers must provide regardless of company size.
Part-time workforce challenges affect many grocery stores that rely heavily on part-time employees to manage labor costs and scheduling flexibility. ACA requirements focus on full-time equivalent employees, allowing stores to potentially avoid mandate obligations through workforce structuring.
Competitive pressures in local labor markets influence grocery store health insurance decisions, with stores in tight labor markets often needing to offer competitive benefits packages to attract and retain employees, particularly for specialized positions like butchers, bakers, and department managers.
PRO TIP: Small grocery stores can explore Professional Employer Organization (PEO) arrangements that pool employees with other small businesses to access better health insurance rates and broader benefit options.
State-based considerations affect grocery store health insurance obligations, with some states implementing additional requirements beyond federal mandates. California, Hawaii, and Massachusetts have enacted state-specific employer health insurance requirements that may apply to smaller employers.
IMPORTANT NOTE: Health insurance benefits represent a significant ongoing operational cost that grocery store owners must factor into business planning and pricing strategies, often comprising 15-25% of total payroll costs.
Understanding the relationship between how much is business insurance and employee benefits helps grocery store owners develop comprehensive cost management strategies that balance regulatory compliance with operational sustainability.
FAQ
What is the most important grocery store insurance for a grocery store?
General liability insurance represents the most critical grocery store insurance coverage for grocery stores, protecting against customer slip-and-fall accidents, foodborne illness claims, and property damage incidents. This coverage is often required by commercial leases and provides the foundation for protecting business assets against third-party claims that can result in significant financial losses.
Workers’ compensation insurance ranks equally important for stores with employees, as it’s legally mandated in most states and protects both employees and employers from work-related injury costs. Combined, these two grocery store insurance coverage types address the highest frequency and severity risks facing grocery operations.
How can grocery stores reduce insurance costs?
Implementing comprehensive safety programs, installing security systems, and maintaining clean, well-maintained premises can qualify grocery stores for significant insurance discounts. Many carriers offer premium reductions of 10-25% for stores with certified safety training programs, surveillance cameras, and slip-resistant flooring.
Bundling multiple coverage types into Business Owner’s Policies (BOPs) typically costs less than purchasing separate policies. Additionally, higher deductibles can reduce premiums, though stores must ensure they can afford the out-of-pocket costs if claims occur.
Do grocery stores need product liability insurance?
Yes, grocery stores need product liability protection to defend against claims that sold products caused illness or injury to customers. While this coverage is often included in general liability policies, stores selling prepared foods, operating delis, or carrying high-risk products may need enhanced product liability coverage.
Product liability insurance protects your business if one of your products ever causes damage or personal injury and may cover expenses of recovery in situations where a product needs to be recalled, making it essential for comprehensive risk management.
What factors affect grocery store insurance costs most?
Store location, size, claims history, and specific operations represent the primary factors influencing grocery store insurance costs. Stores in high-crime areas or regions prone to natural disasters pay substantially higher premiums, while claim-free operations may qualify for significant discounts.
The type of products sold also impacts costs, with stores selling alcohol, operating pharmacies, or preparing foods facing higher liability exposures and corresponding premium increases. Employee count and payroll levels directly affect workers’ compensation costs.
Is cyber insurance necessary for small grocery stores?
Cyber insurance has become essential for grocery stores processing credit card transactions and maintaining customer databases. Grocery stores and other retail business owners pay an average of $57 per month, or $683 annually, for cyber insurance protecting against data breaches and business interruption from cyber attacks.
Even small stores face significant exposure from payment card industry (PCI) compliance failures and point-of-sale system breaches that can result in substantial fines and customer notification costs.
How does workers’ compensation work for grocery stores?
Workers’ compensation for grocery stores covers medical expenses and wage replacement for employees injured while performing job duties, from cashiers to stock personnel to deli workers. Workers’ compensation insurance median cost is $123 per month for retail operations, with rates varying based on job classifications and injury history.
Coverage is mandatory in most states and protects employers from employee lawsuits related to work injuries, while ensuring injured workers receive necessary medical care and income support during recovery periods.
Conclusion
Grocery store insurance requirements in 2025 reflect the evolving complexity of food retail operations, with comprehensive protection essential for financial stability and regulatory compliance. Business Owner’s Policies averaging $87-95 monthly provide cost-effective bundled coverage for most independent grocery operations, while specialized coverage addresses unique risks including product liability, cyber threats, and business interruption from equipment failures.
The changing commercial insurance landscape, with average premium increases of 5.2% across all account sizes in Q2 2024, requires grocery store owners to actively manage their insurance programs through regular coverage reviews, risk management implementation, and strategic carrier relationships that balance protection needs with cost management objectives.
Key Takeaways
Essential Coverage Requirements: Grocery stores need general liability, workers’ compensation, commercial property, and cyber liability insurance as fundamental protection against operational risks, with Business Owner’s Policies providing cost-effective bundled coverage for most independent operations.
Cost Management Strategies: Implementing safety programs, security measures, and risk management protocols can reduce insurance costs by 10-25% while improving overall operational safety and reducing claim frequency.
Regulatory Compliance: Federal and state insurance requirements vary significantly by location and business size, making it essential to work with licensed insurance professionals familiar with local grocery industry regulations and mandatory coverage levels.
Specialized Risk Protection: Unique grocery industry exposures including spoilage coverage, equipment breakdown protection, and product liability require specialized coverage beyond standard retail insurance policies.
Ongoing Risk Management: Regular insurance reviews, claims analysis, and coverage adjustments ensure protection remains adequate as business operations evolve and industry risks change over time.
Disclaimer
Data Freshness: Insurance rates and regulations change frequently. Premium data presented reflects 2024-2025 market conditions and may vary significantly based on individual business characteristics, location, and carrier underwriting guidelines. Data accuracy depends on timing of official industry releases and regulatory updates.
Geographic Variations: Insurance requirements vary significantly by state, with workers’ compensation, liquor liability, and business registration requirements differing across jurisdictions. Always consult your state’s insurance department and regulatory agencies for specific local requirements affecting your grocery store operations.
Professional Advice: This information is for educational purposes only and does not constitute insurance or legal advice. Insurance coverage decisions should be made in consultation with licensed insurance professionals familiar with grocery industry risks and current market conditions. Individual coverage needs vary based on specific business operations, location, and risk tolerance