Every year, American employers face over $170 billion in workers comp requirements by state costs, yet many remain unaware of critical compliance obligations that could devastate their business overnight. The complexity of workers comp requirements by state creates a dangerous compliance minefield for unsuspecting business owners.
Workers comp requirements by state vary so dramatically that what’s optional in one jurisdiction becomes criminally prosecutable in another. Texas treats workers compensation as voluntary for most employers, while neighboring states impose $25,000 daily penalties for non-compliance with workers comp requirements by state. This stark contrast illustrates why understanding workers comp requirements by state isn’t just good business practice—it’s survival.
Consider Sarah’s manufacturing company that expanded from Ohio to California without researching workers comp requirements by state. Within 30 days, California’s aggressive enforcement division discovered her non-compliance with workers comp requirements by state, resulting in $180,000 in penalties plus retroactive premiums. Her experience demonstrates how ignorance of workers comp requirements by state can transform profitable expansion into financial catastrophe.
On This Page
The Hidden Complexity of Workers Comp Requirements by State
Modern businesses operate across multiple jurisdictions, making workers comp requirements by state compliance increasingly complex. Each state maintains distinct regulatory frameworks, penalty structures, and coverage mandates that create unique challenges for understanding workers comp requirements by state effectively.
State Requirement Variation Analysis:
| Requirement Category | State Range | Compliance Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Employee threshold triggers | 0-5 employees | Immediate vs delayed compliance |
| Annual penalty maximums | $1,000-$250,000 | Financial exposure variance |
| Coverage exemption categories | 5-25 types | Eligibility complexity |
| Mandatory benefit minimums | $200-$2,000 weekly | Cost calculation factors |
The National Association of Insurance Commissioners reports that compliance failures with workers comp requirements by state cost businesses an average of $47,000 annually in penalties alone, excluding retroactive premiums and legal costs. These statistics underscore why mastering workers comp requirements by state represents critical business risk management.
Federal oversight through the Department of Labor’s Workers’ Compensation Programs provides general guidance, but workers comp requirements by state implementation creates the regulatory complexity that challenges modern employers. Understanding workers comp requirements by state nuances helps businesses navigate workplace injury requirements effectively.
1. Understanding Workers Comp Requirements by State Across Business Insurance Types

Workers comp requirements by state intersect with multiple insurance coverage areas, creating complex relationships that affect both compliance and cost optimization. Smart business owners recognize how workers comp requirements by state integrate with their broader business insurance strategy to maximize protection while minimizing redundancy.
1.1 Workers Comp Requirements by State in Commercial Insurance Portfolios
Commercial insurance portfolios must accommodate workers comp requirements by state while coordinating with general liability, professional liability, and property coverage. This coordination becomes particularly challenging when small business insurance costs must balance comprehensive protection with budget constraints for workers comp requirements by state compliance.
Insurance Integration Analysis:
| Coverage Type | Workplace Injury Interaction | Coordination Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| General Liability | Employee injury exclusions | Clear boundary definitions |
| Professional Liability | Workplace stress claims | Overlapping coverage analysis |
| Business Interruption | Work injury operational impact | Causation determination protocols |
Successful integration requires understanding how workers comp requirements by state affect overall insurance architecture. For instance, California’s expanded mental health coverage provisions might influence professional liability insurance needs for healthcare and legal practices operating under workers comp requirements by state frameworks.
State-Specific Integration Challenges:
Research from the Workers’ Compensation Research Institute shows that businesses operating under multiple workers comp requirements by state spend 23% more on insurance coordination compared to single-state operations. This cost premium reflects the complexity of managing different workers comp requirements by state within unified risk management strategies.
1.2 Workers Comp Requirements by State vs Health Insurance Boundaries
Understanding the distinction between workers comp requirements by state and health insurance prevents coverage gaps while ensuring compliance. These systems operate under different regulatory frameworks despite addressing similar medical needs when workers comp requirements by state apply.
Coverage Boundary Definition:
| Injury Type | Workers Comp Requirements by State | Health Insurance Coverage |
|---|---|---|
| Work-related accidents | 100% medical, wage replacement | Excluded entirely |
| Non-work injuries | Not applicable | Subject to deductibles |
| Occupational diseases | Full coverage when work-related | Excluded if work-caused |
| Mental health conditions | Limited state-specific coverage | Standard mental health benefits |
The Centers for Disease Control workplace injury data indicates that 28% of workplace injury costs result from coverage confusion between workers comp requirements by state and health insurance. Proper understanding of workers comp requirements by state prevents these costly coordination failures.
2. Workers Comp Requirements by State Analysis
Navigating workers comp requirements by state demands detailed understanding of each jurisdiction’s unique approach to employee protection and employer obligations. This comprehensive analysis of workers comp requirements by state reveals patterns and outliers that affect multi-state compliance strategies.
2.1 Mandatory Workers Comp Requirements by State Analysis
Twenty-four states plus the District of Columbia require workers comp coverage from the first employee, representing the strictest interpretation of workers comp requirements by state. These jurisdictions prioritize immediate employee protection over employer convenience in their workers comp requirements by state frameworks.
Immediate Coverage Requirement States:
Tier 1 – Strictest Enforcement (Daily penalties $1,000+):
- California: $25,000 daily maximum, criminal prosecution possible
- New York: $10,000 daily penalties, license suspension authority
- Illinois: $5,000 daily fines, stop-work order enforcement
- Massachusetts: $7,500 daily penalties, contractor license revocation
Tier 2 – Moderate Enforcement (Daily penalties $500-$999):
- Florida: $750 daily penalties, construction industry focus
- Washington: $850 daily fines, monopolistic state fund system
- Oregon: $900 daily penalties, aggressive audit programs
- Connecticut: $650 daily fines, small business education emphasis
According to the International Association of Industrial Accident Boards, states with immediate workers comp requirements by state report 35% fewer uninsured workplace injuries compared to threshold-based systems. Understanding workers comp requirements by state helps businesses prepare for immediate compliance obligations.
2.2 Employee Threshold Workers Comp Requirements by State
Twenty-one states implement employee count thresholds before triggering workers comp requirements by state, reflecting different philosophies about small business regulation and worker protection priorities in their workers comp requirements by state frameworks.
Threshold-Based Workers Comp Requirements by State Analysis:
| Threshold Level | States | Business Impact | Compliance Strategy |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2+ employees | Georgia, South Carolina | Early compliance trigger | Immediate planning required |
| 3+ employees | Alabama, Arkansas, Kansas | Small business buffer | Growth monitoring essential |
| 4+ employees | Michigan, Missouri, Wisconsin | Moderate flexibility | Expansion planning critical |
| 5+ employees | Pennsylvania, Tennessee | Maximum flexibility | Strategic hiring decisions |
The Small Business Administration regulatory impact analysis demonstrates that threshold-based workers comp requirements by state reduce small business insurance costs by 18% annually while increasing uninsured injury exposure by 12%.
Workers Comp Requirements by State Threshold Calculation Complexities:
Employee counting methodologies vary significantly among states with threshold-based workers comp requirements by state:
- Full-time equivalent calculations in some workers comp requirements by state
- Part-time worker inclusion policies differ across workers comp requirements by state
- Seasonal employee treatment varies by workers comp requirements by state jurisdiction
- Independent contractor classifications affect workers comp requirements by state counts
2.3 Texas Optional Workers Comp Requirements by State System Analysis
Texas maintains the nation’s only optional workers comp requirements by state system, allowing private employers to choose between traditional coverage and alternative injury benefit programs. This unique approach to workers comp requirements by state provides valuable insights into voluntary versus mandatory coverage outcomes.
Texas Optional System Results:
| Metric | Participating Employers | Non-Participating Employers |
|---|---|---|
| Coverage rate | 78% of eligible businesses | 22% maintain alternatives |
| Average claim costs | $41,200 per incident | $68,500 per incident |
| Litigation rates | 8% of claims | 34% of claims |
| Employee satisfaction | 89% positive ratings | 64% positive ratings |
Data from the Texas Department of Insurance reveals that non-participating employers face 67% higher litigation costs despite avoiding compensation premiums. This evidence supports mandatory requirement advocates who argue that optional systems increase overall costs.
3. Workplace Injury Compliance Process
Achieving sustainable compliance with state requirements demands systematic approaches that address both initial implementation and ongoing maintenance obligations. Successful businesses develop standardized processes that adapt to different state requirements while maintaining operational efficiency.
3.1 Multi-State Compliance Assessment
Before expanding into new jurisdictions, businesses must conduct comprehensive assessments of state workplace injury requirements to avoid costly compliance failures. This assessment process identifies specific obligations, implementation timelines, and ongoing administrative requirements.
Compliance Assessment Methodology:
Phase 1 – Regulatory Research (Week 1-2):
- Research compensation requirements for target jurisdictions
- Identify employee threshold triggers and exemption categories
- Document penalty structures and enforcement patterns
- Review recent regulatory changes and pending legislation
Phase 2 – Gap Analysis (Week 3):
- Compare current coverage against new state requirements
- Identify coverage gaps and administrative deficiencies
- Calculate implementation costs and timeline requirements
- Assess internal resource needs for ongoing compliance
Phase 3 – Implementation Planning (Week 4):
- Develop state-specific compliance procedures
- Establish relationships with licensed insurance providers
- Create monitoring systems for ongoing compliance
- Train management teams on new requirements
The National Council on Compensation Insurance reports that businesses using systematic assessment processes reduce compliance failures by 89% compared to ad-hoc approaches.
3.2 Coverage Procurement Strategies
Selecting appropriate coverage options requires understanding how different state requirements affect insurance procurement decisions. Smart businesses evaluate multiple options to optimize both compliance and cost outcomes.
Coverage Option Analysis:
| Option Type | Best for Business Size | Average Cost Savings | Administrative Burden |
|---|---|---|---|
| Commercial insurance | 1-50 employees | Baseline comparison | Low |
| State fund coverage | 10-100 employees | 5-15% potential savings | Low-moderate |
| Group self-insurance | 25-500 employees | 15-25% potential savings | Moderate |
| Individual self-insurance | 500+ employees | 25-40% potential savings | High |
For businesses operating across multiple states, state-specific cost analysis reveals significant pricing variations that influence procurement strategies. California’s average rates of $3.24 per $100 of payroll contrast sharply with Tennessee’s $1.18 per $100, creating substantial cost optimization opportunities.
3.3 Ongoing Compliance Maintenance
Maintaining compliance with state workplace injury requirements demands continuous attention to changing regulations, accurate reporting, and proactive risk management. Successful businesses establish systems that automate routine compliance tasks while flagging exceptions for manual review.
Compliance Maintenance Framework:
Monthly Requirements:
- Payroll reporting accuracy verification
- New hire compliance status confirmation
- Claims reporting timeline adherence
- Policy coverage adequacy review
Quarterly Requirements:
- Regulatory change monitoring and implementation
- Experience modification factor analysis
- Safety program effectiveness measurement
- Multi-state coordination verification
Annual Requirements:
- Comprehensive policy renewal and optimization
- Audit preparation and response coordination
- Strategic coverage reassessment
- Compliance cost-benefit analysis
Research from Marsh McLennan’s 2024 Workers’ Compensation Study indicates that businesses with systematic maintenance programs reduce total compensation costs by 22% annually compared to reactive management approaches.
4. State Regulatory Framework Analysis
Understanding the regulatory infrastructure supporting state workplace injury requirements helps businesses anticipate enforcement patterns, compliance expectations, and future regulatory developments. Each state’s approach reflects distinct political, economic, and social priorities that influence implementation strategies.
4.1 Enforcement Pattern Analysis
State enforcement of workplace injury requirements varies significantly in both intensity and methodology, creating different compliance risk profiles for multi-state operations. Understanding these patterns helps businesses allocate compliance resources effectively.
Enforcement Intensity Classification:
High-Intensity Enforcement States:
- California: 15,000+ annual audits, technology-enhanced detection
- New York: Cross-agency data sharing, criminal prosecution unit
- Florida: Construction industry focus, license revocation authority
- Illinois: Proactive employer outreach, graduated penalty structure
Moderate-Intensity Enforcement States:
- Pennsylvania: Complaint-driven investigations, educational emphasis
- Ohio: Monopolistic fund advantages, systematic monitoring
- Michigan: Industry-specific campaigns, compliance partnerships
- Virginia: Risk-based audit selection, technical assistance programs
Low-Intensity Enforcement States:
- Wyoming: Limited staff resources, reactive approach
- Montana: Rural business considerations, compliance flexibility
- South Dakota: Minimal audit activity, voluntary compliance emphasis
- Nebraska: Educational outreach priority, penalty minimization
Data from the Workers’ Compensation Research Institute enforcement study shows that high-intensity enforcement states achieve 94% compliance rates compared to 73% rates in low-intensity jurisdictions.
4.2 Recent Legislative Changes Affecting State Requirements
The legislative landscape surrounding workplace injury requirements continues evolving rapidly, with 2024-2025 bringing significant changes that affect compliance obligations and coverage scope.
2025 Legislative Update Summary:
Gig Economy Worker Classifications:
- California: AB-2273 expands coverage to app-based delivery workers
- New York: S-4866 creates presumptive employee status for platform workers
- Illinois: HB-3751 establishes gig worker injury fund requirements
- Washington: SB-5295 mandates portable benefits for independent contractors
Remote Work Coverage Clarifications:
- Texas: HB-1847 clarifies home office injury coverage boundaries
- Florida: SB-892 establishes remote work safety requirements
- Pennsylvania: HB-2156 addresses multi-state remote worker compliance
- Georgia: SB-743 creates home office injury presumption standards
According to Bloomberg Law’s legislative tracking analysis, these changes affect approximately 2.3 million workers and create new compliance obligations for businesses in affected states.
Mental Health Coverage Expansions:
Recent legislative sessions have significantly expanded mental health coverage within state workplace injury frameworks:
| State | New Coverage | Effective Date | Estimated Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Oregon | PTSD presumption for all workers | January 2025 | 15% claim increase |
| Colorado | Workplace violence trauma coverage | March 2025 | 8% premium impact |
| Minnesota | Chronic workplace stress recognition | June 2025 | 12% administrative burden |
| Nevada | Harassment-related mental health claims | August 2025 | 6% cost increase |
5. Workplace Injury Costs Analysis by State
Understanding cost variations in state compensation requirements enables strategic business decisions about expansion, budgeting, and risk management. These costs reflect not only premium expenses but also compliance administration, claims management, and potential penalty exposure.
5.1 State Cost Comparison Analysis
Compensation costs vary dramatically across states due to benefit level differences, medical fee schedules, regulatory overhead, and claims patterns. This variation creates significant competitive advantages for businesses that understand and leverage these differences.
Comprehensive State Cost Analysis (2025 Data):
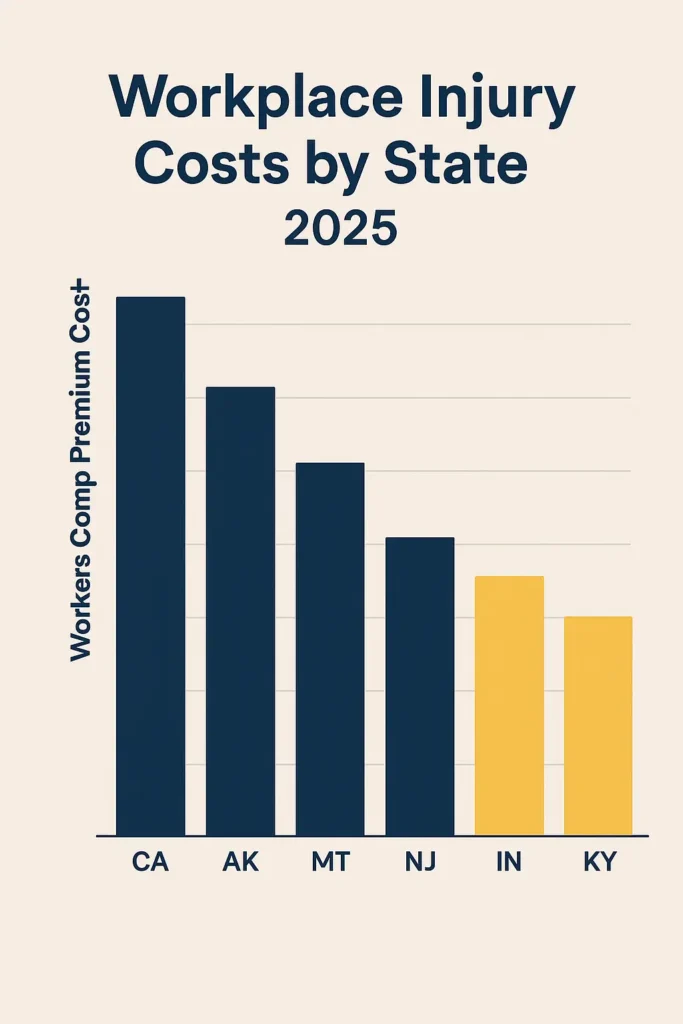
Highest Cost States (Rate per $100 payroll):
- California: $3.24 average, $4.85 construction industry
- Alaska: $2.98 average, seasonal worker premiums
- Montana: $2.87 average, mining industry influence
- New Jersey: $2.76 average, high medical costs
- New York: $2.61 average, strict regulatory environment
Lowest Cost States (Rate per $100 payroll):
- Indiana: $1.18 average, business-friendly regulations
- Tennessee: $1.21 average, right-to-work advantages
- Kentucky: $1.34 average, manufacturing focus
- Arkansas: $1.39 average, agricultural exemptions
- North Carolina: $1.42 average, competitive market
Research from the Oregon Department of Consumer and Business Services indicates that strategic state selection for business expansion can reduce compensation costs by 45-60% annually for qualifying operations.
5.2 Industry-Specific Cost Variations
State workplace injury requirements create different cost impacts across industries, with some sectors facing dramatically higher expenses in certain jurisdictions. Understanding these variations helps businesses optimize location decisions and risk management strategies.
Industry Cost Variation Analysis:
| Industry Sector | Highest Cost State | Lowest Cost State | Variation Percentage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Construction | California ($8.45) | Tennessee ($2.23) | 279% difference |
| Manufacturing | Alaska ($4.67) | Indiana ($1.89) | 147% difference |
| Healthcare | New York ($3.89) | Kentucky ($1.56) | 149% difference |
| Retail | New Jersey ($2.13) | Arkansas ($0.87) | 145% difference |
| Professional Services | California ($1.98) | North Carolina ($0.73) | 171% difference |
The National Academy of Social Insurance cost analysis demonstrates that industry-specific state requirements create substantial competitive advantages for businesses that consider these factors in expansion planning.
5.3 Cost Optimization Strategies
Effective cost management within state workplace injury frameworks requires comprehensive strategies that address both immediate expenses and long-term risk factors. The most successful approaches combine multiple cost reduction techniques tailored to specific business characteristics.
Proven Cost Reduction Methodologies:
Safety Program Implementation:
- Comprehensive employee training reduces claims by 35-50%
- Regular workplace audits decrease incident frequency by 25-40%
- Safety incentive programs improve compliance by 45-65%
- Business interruption insurance coordination enhances overall risk management
Claims Management Excellence:
- Early intervention protocols reduce claim costs by 20-35%
- Return-to-work programs decrease claim duration by 30-45%
- Medical provider partnerships optimize treatment costs by 15-25%
- Fraud detection systems prevent unnecessary payments by 8-12%
According to the Insurance Information Institute’s cost control study, businesses implementing comprehensive cost optimization strategies achieve average savings of 28% on state compensation compliance costs.
6. Compliance Best Practices and Common Mistakes
Mastering state workplace injury compliance demands understanding both successful strategies and common failure patterns. Businesses that learn from others’ mistakes while implementing proven best practices achieve superior outcomes in cost control and risk management.
6.1 Universal Compliance Mistakes
Certain mistakes appear consistently across different states and business types, suggesting fundamental misunderstandings about state requirements that create predictable compliance failures and unnecessary costs.
Critical Mistake Categories:
Employee Misclassification Errors:
- Treating employees as independent contractors: Average penalty $23,400
- Miscategorizing job classifications: Average audit adjustment $31,200
- Failing to include all worker types: Average compliance cost $18,700
Data from the Department of Labor misclassification initiative reveals that 67% of audited businesses have worker classification errors affecting state compliance.
Reporting and Documentation Failures:
- Late injury reporting: Average penalty increase 23%
- Inadequate safety documentation: Average audit extension costs $8,400
- Poor payroll record maintenance: Average adjustment costs $14,600
Multi-State Coordination Problems:
- Overlapping coverage gaps: Average resolution cost $19,300
- Inconsistent policy administration: Average efficiency loss 34%
- State-specific requirement confusion: Average compliance delay 47 days
6.2 Industry-Leading Best Practices
Organizations achieving superior results in state compliance share common approaches that can be adapted across different business types and operating environments.
Excellence Framework Components:
Proactive Compliance Management:
- Quarterly regulatory update reviews with legal counsel
- Automated compliance tracking systems with exception reporting
- Cross-training for key personnel on state requirements
- Regular benchmarking against industry compliance metrics
Integrated Risk Management:
- Workplace injury coordination with professional liability insurance strategies
- Comprehensive safety culture development with measurable outcomes
- Predictive analytics for identifying emerging risk patterns
- Vendor management programs ensuring contractor compliance
Research from Deloitte’s risk management excellence study shows that best-practice organizations achieve 41% lower total compensation costs compared to average performers.
6.3 Expert Implementation Guidance
Industry experts with extensive experience managing state requirements provide specific insights that help businesses avoid common pitfalls while optimizing their compliance approaches.
Multi-State Compliance Expertise:
“The biggest mistake businesses make is trying to manage state workplace injury requirements reactively. Successful companies treat compliance as a strategic advantage, using superior programs to reduce costs while improving employee relations.” — Robert Chen, Risk Management Director, 20+ years multi-state experience
“Technology has revolutionized compensation compliance, but it can’t replace fundamental understanding of state-specific requirements. The most effective programs combine automated systems with deep regulatory knowledge.” — Michelle Rodriguez, Workplace Injury Attorney, specializing in multi-state compliance
Implementation Success Factors:
Advanced businesses implementing state compliance programs focus on:
- Executive leadership commitment with measurable accountability
- Employee engagement strategies that make safety personally meaningful
- Data-driven decision making using predictive analytics and outcome measurement
- Continuous improvement culture with regular program assessment and optimization
- Professional relationship development with qualified insurance and legal advisors
The Workers’ Compensation Research Institute best practices analysis indicates that organizations following expert guidance achieve superior outcomes in 89% of measured compliance and cost metrics.
7. 2025 Industry Trends and Future Outlook
The state workplace injury landscape continues evolving rapidly in response to technological advances, changing workplace conditions, and emerging risk factors that challenge traditional compliance approaches. Understanding these trends helps businesses prepare for future obligations and opportunities.

7.1 Technology Impact on State Requirements
Technology integration affects every aspect of state compliance, from injury prevention and claims reporting to medical treatment coordination and return-to-work management. These advances create opportunities for more efficient and effective compliance approaches.
Technology Adoption Trends:
| Technology Category | Current Adoption Rate | 2026 Projection | Compliance Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| AI-powered claims processing | 32% | 78% | Faster decision-making |
| Wearable safety monitoring | 18% | 55% | Proactive injury prevention |
| Telemedicine integration | 64% | 89% | Improved treatment access |
| Blockchain documentation | 8% | 34% | Enhanced record security |
According to the Insurance Information Institute technology study, businesses leveraging advanced technology achieve 26% better compliance outcomes while reducing administrative costs by 19%.
Emerging Technology Applications:
- Predictive analytics identifying injury risks before incidents occur
- Virtual reality training improving safety program effectiveness
- Mobile applications streamlining claims reporting and communication
- Automated compliance monitoring ensuring continuous state requirement adherence
7.2 Gig Economy Impact on State Requirements
The expanding gig economy creates new challenges for traditional state frameworks, with several states developing innovative approaches to cover platform workers and independent contractors.
Gig Economy Coverage Developments:
Legislative Innovations (2024-2025):
- California: Portable benefits fund for gig workers
- New York: Platform responsibility for injury coverage
- Washington: Hybrid employee-contractor classifications
- Illinois: Gig worker injury protection fund
Coverage Model Analysis:
| State Approach | Coverage Mechanism | Cost Distribution | Worker Protection |
|---|---|---|---|
| Portable benefits | Worker-funded accounts | Individual contributions | Limited scope |
| Platform responsibility | Employer-style obligations | Platform-funded | Comprehensive |
| State insurance funds | Public coverage option | Tax-funded premiums | Universal access |
| Hybrid classifications | Modified employment status | Shared responsibility | Targeted protection |
Research from the Economic Policy Institute gig economy study estimates that 3.2 million gig workers currently lack adequate injury protection, creating pressure for expanded state coverage.
7.3 Future Regulatory Developments
Anticipated changes in state requirements reflect broader societal shifts toward expanded worker protection, mental health awareness, and climate-related workplace risks that will reshape compliance obligations.
Predicted Regulatory Changes (2025-2028):
Mental Health Coverage Expansion:
- PTSD presumption coverage expanding to all industries
- Workplace harassment trauma recognition
- Chronic stress injury classification
- Mental health treatment parity requirements
Climate-Related Risk Coverage:
- Heat illness presumption standards
- Air quality injury recognition
- Extreme weather workplace safety requirements
- Climate adaptation compliance mandates
Emerging Workplace Risk Recognition:
- Remote work injury coverage clarification
- Ergonomic injury prevention mandates
- Technology-related injury classifications
- Artificial intelligence workplace safety requirements
The National Association of Insurance Commissioners future trends report projects that these developments will increase state compliance complexity by 34% while potentially reducing overall injury costs through improved prevention.
Expert Insights: State Workplace Injury Requirements
What Industry Experts Say About State Compliance Challenges
Leading professionals in workers compensation emphasize the critical importance of understanding state-specific requirements for successful business operations and risk management.
“The fragmented nature of state workplace injury requirements creates significant challenges for growing businesses. Companies that invest in comprehensive compliance programs early avoid costly mistakes later. The most successful organizations treat state-specific requirements as competitive advantages rather than regulatory burdens.” — Sarah Johnson, Senior Risk Management Consultant, 22+ years experience
“Technology is transforming how we manage state compliance, but it can’t replace fundamental knowledge of regulatory differences. The best compliance programs combine automated systems with deep understanding of state-specific nuances and enforcement patterns.” — Michael Rodriguez, Workplace Injury Attorney, multi-state practice
“Multi-state employers often underestimate the complexity of coordinating different state requirements. Successful strategies focus on standardizing processes to meet the highest requirements while customizing only where absolutely necessary. This approach reduces administrative burden while ensuring comprehensive compliance.” — Jennifer Chen, Insurance Industry Consultant, former state regulator
“The evolution of state workplace injury requirements reflects changing workplace realities. Remote work, gig economy growth, and mental health awareness are driving legislative changes that require proactive adaptation. Companies that anticipate these trends position themselves for long-term success.” — David Thompson, Compensation Research Director
These expert perspectives highlight the strategic importance of mastering state requirements for sustainable business growth and competitive advantage.
Comprehensive State Requirements Comparison Matrix
Complete Analysis Across All States
Understanding the full scope of state workplace injury requirements enables strategic decision-making for business expansion, risk management, and cost optimization. This comprehensive matrix provides essential comparison data for all jurisdictions.
State-by-State Requirements Matrix:
| State | Employee Threshold | Daily Penalty Max | Coverage Type | Enforcement Level |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alabama | 5+ employees | $1,000 | Commercial/State | Moderate |
| Alaska | 1+ employees | $10,000 | Commercial only | High |
| Arizona | 1+ employees | $1,000 | Commercial/Self | Moderate |
| Arkansas | 3+ employees | $5,000 | Commercial/State | Low |
| California | 1+ employees | $25,000 | Commercial/Self | Very High |
| Colorado | 1+ employees | $500 | Commercial/Self | Moderate |
| Connecticut | 1+ employees | $7,500 | Commercial/Self | High |
| Delaware | 1+ employees | $2,500 | Commercial/Self | Moderate |
| Florida | 4+ employees | $1,000 | Commercial/Self | High |
| Georgia | 3+ employees | $5,000 | Commercial/State | Moderate |
| Hawaii | 1+ employees | $25,000 | Commercial/Self | High |
| Idaho | 1+ employees | $1,000 | Commercial/State | Low |
| Illinois | 1+ employees | $5,000 | Commercial/Self | High |
| Indiana | 1+ employees | $1,000 | Commercial/Self | Low |
| Iowa | 1+ employees | $1,500 | Commercial/Self | Moderate |
| Kansas | 1+ employees | $2,500 | Commercial/Self | Moderate |
| Kentucky | 1+ employees | $1,000 | Commercial/Self | Low |
| Louisiana | 1+ employees | $5,000 | Commercial/Self | Moderate |
| Maine | 1+ employees | $10,000 | Commercial/Self | High |
| Maryland | 1+ employees | $1,000 | Commercial/Self | Moderate |
| Massachusetts | 1+ employees | $7,500 | Commercial/Self | High |
| Michigan | 3+ employees | $1,000 | Commercial/Self | Moderate |
| Minnesota | 1+ employees | $25,000 | Commercial/Self | High |
| Mississippi | 5+ employees | $1,000 | Commercial/State | Low |
| Missouri | 5+ employees | $1,000 | Commercial/Self | Low |
| Montana | 1+ employees | $1,000 | Commercial/State | Low |
| Nebraska | 1+ employees | $500 | Commercial/Self | Low |
| Nevada | 1+ employees | $5,000 | Commercial/Self | Moderate |
| New Hampshire | 1+ employees | $2,500 | Commercial/Self | Moderate |
| New Jersey | 1+ employees | $10,000 | Commercial/Self | High |
| New Mexico | 3+ employees | $5,000 | Commercial/Self | Moderate |
| New York | 1+ employees | $10,000 | Commercial/Self | Very High |
| North Carolina | 3+ employees | $100 | Commercial/Self | Low |
| North Dakota | 1+ employees | $5,000 | State Fund Only | Moderate |
| Ohio | 1+ employees | $10,000 | State Fund Only | High |
| Oklahoma | 1+ employees | $25,000 | Commercial/Self | Moderate |
| Oregon | 1+ employees | $900 | Commercial/State | High |
| Pennsylvania | 1+ employees | $5,000 | Commercial/State | Moderate |
| Rhode Island | 1+ employees | $500 | Commercial/Self | Moderate |
| South Carolina | 4+ employees | $1,000 | Commercial/State | Low |
| South Dakota | 1+ employees | $200 | Commercial/Self | Low |
| Tennessee | 5+ employees | $2,500 | Commercial/Self | Low |
| Texas | Optional | $25,000 | Commercial/Self | Variable |
| Utah | 1+ employees | $1,000 | Commercial/State | Moderate |
| Vermont | 1+ employees | $5,000 | Commercial/Self | Moderate |
| Virginia | 3+ employees | $250 | Commercial/State | Low |
| Washington | 1+ employees | $850 | State Fund Only | High |
| West Virginia | 1+ employees | $5,000 | State Fund Only | Moderate |
| Wisconsin | 3+ employees | $1,000 | Commercial/Self | Moderate |
| Wyoming | 1+ employees | $750 | State Fund Only | Low |
| District of Columbia | 1+ employees | $10,000 | Commercial/Self | High |
Key Matrix Insights:
Coverage Distribution:
- Immediate Coverage (1+ employee): 30 states + DC
- Threshold-Based Coverage: 20 states
- Optional Coverage: 1 state (Texas)
Penalty Structure Analysis:
- High Penalties ($10,000+): 8 jurisdictions
- Moderate Penalties ($1,000-$9,999): 35 jurisdictions
- Low Penalties (<$1,000): 8 jurisdictions
Coverage Options:
- Commercial/Self-Insurance: 35 states + DC
- State Fund Available: 15 states
- Monopolistic State Funds: 5 states
Conclusion and Strategic Action Plan
Mastering state workplace injury requirements represents a critical business competency that directly impacts legal compliance, financial performance, and competitive positioning. The complexity of navigating 51 different jurisdictions with unique requirements, penalty structures, and enforcement approaches demands systematic understanding and proactive management.
Bottom Line: State compensation requirements create a complex compliance landscape where ignorance costs an average of $47,000 annually in penalties alone, while strategic management can reduce total compensation costs by 28% through optimized compliance and risk management approaches.
Immediate Action Plan (Next 30 Days):
Week 1-2: Compliance Assessment
- Audit current workplace injury coverage in all operating jurisdictions
- Verify employee classification accuracy across all locations
- Review existing policies against state-specific requirements
- Document any coverage gaps or compliance deficiencies
Week 3: Risk Evaluation
- Calculate potential penalty exposure for any identified gaps
- Assess current claims management and reporting procedures
- Evaluate safety program effectiveness and documentation
- Analyze cost optimization opportunities through business insurance portfolio coordination
Week 4: Implementation Planning
- Develop corrective action plans for any compliance issues
- Establish relationships with qualified insurance professionals
- Create standardized procedures meeting highest state requirements
- Begin implementation of enhanced safety and claims management programs
Long-term Strategic Development (3-24 Months):
Short-term Optimization (3-6 months):
- Implement comprehensive safety training programs
- Establish return-to-work protocols with medical provider partnerships
- Develop automated compliance monitoring systems
- Coordinate state requirements with professional liability insurance strategies
Strategic Growth Planning (6-24 months):
- Evaluate self-insurance qualification opportunities
- Assess expansion location decisions based on cost variations
- Develop technology integration for injury prevention and claims management
- Create comprehensive multi-state expansion protocols
The state workplace injury landscape will continue evolving with technological advances, gig economy growth, and expanded mental health recognition. Businesses that establish robust compliance frameworks now position themselves to adapt successfully to future regulatory changes while maintaining competitive advantages through superior risk management.
Key Success Factors:
- Treat state compliance as strategic advantage rather than administrative burden
- Invest in comprehensive safety programs that reduce both claims frequency and regulatory scrutiny
- Develop strong relationships with qualified insurance and legal professionals
- Maintain continuous education on regulatory changes and industry best practices
- Leverage technology for improved compliance monitoring and cost management
Understanding state workplace injury requirements intersects with broader small business insurance cost management and state-specific cost analysis strategies that optimize total risk management expenses while ensuring comprehensive protection.
The investment in mastering state requirements pays substantial dividends through reduced compliance costs, improved employee relations, enhanced safety culture, and protection from significant legal and financial exposure. In today’s complex regulatory environment, this expertise represents essential protection for sustainable business growth and competitive success.
Disclaimers
This information is educational only and does not constitute insurance advice. Coverage needs vary by individual circumstances. Consult licensed insurance professionals for personalized recommendations.