Running a small business in 2025 means facing digital threats that can destroy everything you’ve built overnight. Cyber criminals launched over 12,000 confirmed data breaches last year according to the latest industry reports, and they’re specifically hunting small businesses because we’re easier targets.
You might think your local restaurant or consulting firm is too small to notice. That’s exactly what hackers count on. While enterprise companies spend millions on cybersecurity teams, small businesses often run on basic antivirus software and hope for the best.
Here’s what changed in 2025: cyber insurance isn’t optional anymore. It’s become as essential as your general liability coverage or workers’ compensation insurance. The average ransom demand hit $115,000 last year, but total recovery costs often exceed $500,000 when you factor in downtime, customer notifications, and reputation repair.
Quick reality check for small business owners:
- Cyber attacks target SMBs 4x more than large corporations
- 94% of ransomware attacks specifically target backup systems
- One in three small businesses experienced ransomware in 2024
- Recovery time averages 3-6 months for companies without proper coverage
What you’ll learn in this comprehensive guide:
- How cyber insurance for small business actually protects your finances
- Real costs and coverage options that fit small business budgets
- Step-by-step process to qualify for the best rates
- Smart strategies to reduce premiums while maximizing protection
Let’s dive into everything you need to know about protecting your business from cyber threats that could otherwise bankrupt you within weeks.
On This Page
1. Why Small Businesses Need Cyber Insurance More Than Ever
The cyber insurance market reached $15.3 billion globally in 2024, and analysts project it’ll hit $16.3 billion this year. That explosive growth reflects one harsh reality: cyber crime has become the fastest-growing threat to American small businesses.
Think your business is too small for hackers to care? That’s dangerous thinking. Criminals specifically target small companies because you typically lack the security infrastructure that makes attacking larger corporations more difficult and expensive.
Current cyber threat landscape for SMBs:
- Financial services face average monthly premiums of $56 for cyber insurance for small business
- Technology companies pay around $149 monthly due to higher risk exposure
- Healthcare practices need specialized coverage for HIPAA compliance violations
- Retail businesses require protection for customer payment data breaches
1.1 The True Cost of Cyber Attacks on Small Businesses

When cyber criminals target your business, the immediate ransom payment represents just the tip of the iceberg. Recovery expenses quickly spiral into six-figure territory, even for modest-sized companies.
Real financial impact breakdown:
- Forensic investigation costs: $15,000-$50,000
- Legal consultation fees: $10,000-$25,000
- Customer notification expenses: $5,000-$15,000
- Business interruption losses: $20,000-$100,000+
- Reputation management: $10,000-$30,000
Our complete business insurance guide explains how cyber coverage integrates with your existing commercial policies to provide comprehensive protection.
1.2 How Cyber Insurance for Small Business Actually Works
Cyber insurance for small business operates similarly to other commercial coverage types. You pay monthly or annual premiums, and if hackers successfully attack your systems, the insurance company steps in to handle the financial fallout.
Core protection areas:
- First-party coverage handles direct losses to your company
- Third-party liability protects against customer lawsuits
- Business interruption replaces lost income during system downtime
- Regulatory defense covers fines and compliance violations
Unlike traditional business insurance that excludes cyber incidents, specialized cyber insurance for small business fills these critical gaps in your risk management strategy.
1.3 Industries Facing the Highest Cyber Risk Exposure
Certain business sectors attract more cyber criminal attention due to the valuable data they process or store. Understanding your industry’s specific risk profile helps determine appropriate coverage levels.
High-risk industry categories:
- Healthcare providers storing patient records and billing information
- Professional services handling confidential client data
- E-commerce businesses processing credit card transactions
- Technology companies managing customer databases
- Financial advisors accessing investment accounts
Small businesses in these sectors often need our professional liability insurance alongside cyber coverage for complete protection.
2. Types of Cyber Insurance Coverage for Small Businesses
Not all cyber insurance for small business policies offer identical protection. Understanding different coverage types helps you select appropriate protection levels without overpaying for unnecessary features.
2.1 Data Breach Response Coverage
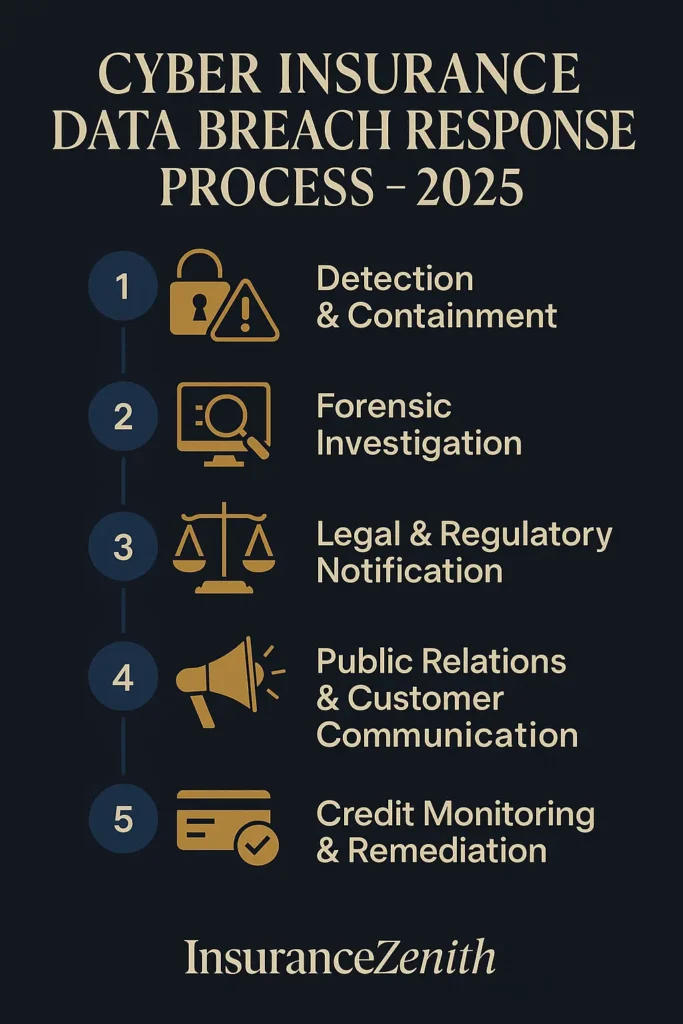
Data breach response represents the most fundamental cyber insurance for small business protection. This coverage kicks in when unauthorized individuals gain access to your customer information, employee records, or business data.
Data breach response includes:
- Forensic investigation services to determine breach scope
- Customer notification services meeting state law requirements
- Credit monitoring for affected individuals
- Public relations support to manage reputation damage
- Legal consultation for regulatory compliance
Cost comparison table:
| Business Size | Average Annual Premium | Typical Coverage Limit |
|---|---|---|
| 1-5 employees | $400-$800 | $100,000-$500,000 |
| 6-25 employees | $800-$1,500 | $500,000-$1,000,000 |
| 26-100 employees | $1,500-$3,000 | $1,000,000-$2,500,000 |
2.2 Business Interruption Cyber Coverage
When hackers disable your computer systems, you can’t serve customers or process orders. Business interruption coverage replaces lost revenue during the recovery period.
This protection becomes especially valuable for businesses heavily dependent on technology for daily operations. Our business interruption insurance article explains how cyber-specific coverage differs from traditional property-based interruption policies.
Business interruption benefits:
- Lost revenue replacement during system downtime
- Extra expense coverage for temporary workarounds
- Employee payroll continuation during recovery
- Vendor payment assistance to maintain relationships
2.3 Cyber Liability and Legal Defense Coverage
Cyber liability protection handles lawsuits filed by customers, business partners, or vendors affected by your data breach. Legal defense costs can quickly consume small business cash flow even if you ultimately win the case.
Liability coverage protects against:
- Customer class-action lawsuits over stolen personal information
- Business partner claims for compromised confidential data
- Regulatory penalties for compliance violations
- Privacy law violation fines and sanctions
For comprehensive liability protection beyond cyber risks, consider our general liability insurance options.
3. How to Choose the Right Cyber Insurance for Small Business
Selecting appropriate cyber insurance for small business requires careful evaluation of your specific risk factors, budget constraints, and coverage needs. Here’s a systematic approach to making smart decisions.
3.1 Conducting Your Business Cyber Risk Assessment
Start by honestly evaluating your current cybersecurity measures and potential vulnerabilities. Most insurance companies require detailed questionnaires about your security practices before providing quotes.
Essential risk assessment questions:
- How many employees have access to sensitive customer data?
- What types of personal information do you collect and store?
- Do you process credit card payments or handle financial data?
- How often do you update software and install security patches?
- Have you experienced any security incidents in the past three years?
Professional risk assessment options:
- Free evaluations from potential insurance providers
- Third-party cybersecurity audits from qualified consultants
- Online vulnerability scanning tools like SecurityScorecard
- Internal IT assessments of current security measures
3.2 Determining Appropriate Coverage Limits
Coverage limits should reflect your potential financial exposure from a cyber incident. Industry experts recommend $1 million in coverage for small businesses handling moderate amounts of customer data.
Factors influencing coverage limit decisions:
- Annual revenue and overall business size
- Volume of customer records and sensitive data
- Industry regulatory requirements and compliance standards
- Potential business interruption costs during system recovery
- Third-party vendor relationships and data sharing agreements
Consider how cyber insurance for small business integrates with your existing commercial policies. Our workers compensation requirements by state guide shows how different coverage types work together for complete protection.
3.3 Comparing Insurance Providers and Policy Terms
The cyber insurance market has become increasingly competitive, giving small businesses more options and better pricing than ever before. Focus on providers with strong financial ratings and experience serving businesses similar to yours.
Key evaluation criteria:
- AM Best financial strength rating of A- or better
- Industry expertise in your business sector
- Claims handling reputation and average response times
- Additional services like risk assessments and employee training
- Policy exclusions and limitations that might affect your coverage
Provider comparison checklist:
| Evaluation Factor | Provider A | Provider B | Provider C |
|---|---|---|---|
| Financial Rating | A+ | A | A- |
| Industry Experience | 15 years | 8 years | 12 years |
| 24/7 Claims Support | Yes | Business hours only | Yes |
| Risk Assessment Included | Yes | Additional cost | Yes |
| Employee Training Resources | Basic | Comprehensive | Basic |
4. Cyber Insurance Requirements and Qualification Process
Insurance companies have significantly tightened their underwriting standards for cyber insurance for small business policies. Understanding these requirements upfront helps you prepare for the application process and secure better rates.
4.1 Essential Security Controls for Coverage Approval

Modern cyber insurance applications require detailed documentation of your cybersecurity measures. Insurance companies use standardized questionnaires to evaluate your risk profile and determine whether to offer coverage.
The five core security requirements:
- Multi-factor authentication (MFA) on all email accounts and administrative systems
- Regular software updates with automated patch management for operating systems
- Employee cybersecurity training with annual refresher courses and testing
- Comprehensive backup strategy including offline or cloud-based storage
- Endpoint protection software on all computers and mobile devices
Advanced requirements for higher-risk businesses:
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) monitoring
- Privileged Access Management (PAM) for critical systems
- Regular penetration testing by qualified security professionals
- Documented incident response plan with emergency contact procedures
- 24/7 Security Operations Center (SOC) monitoring services
4.2 Application Process and Documentation Requirements
The cyber insurance for small business application process typically takes 2-4 weeks from initial inquiry to policy issuance. Thorough preparation can significantly speed up the process and improve your chances of approval.
Required documentation checklist:
- Completed cybersecurity questionnaire with detailed security measures
- Network topology diagrams showing system architecture
- Data inventory listing types and locations of sensitive information
- Employee training records and certification documentation
- Incident response plan with step-by-step procedures
- Third-party vendor security assessments and agreements
Businesses with complex technology needs should also review our commercial vehicle insurance guide if they operate delivery or service vehicles that connect to company networks.
4.3 Common Application Mistakes That Lead to Denial
Insurance companies frequently deny cyber insurance for small business applications due to preventable errors or misrepresentations. Avoiding these common mistakes improves your approval chances and helps secure better rates.
Application denial triggers:
- Incomplete or inaccurate security questionnaire responses
- Lack of documented cybersecurity policies and procedures
- Missing or outdated employee training records
- Previous unreported security incidents or data breaches
- Inadequate backup and recovery testing documentation
Pro tips for successful applications:
- Answer all questions completely and honestly
- Provide specific details about security measures and controls
- Document all cybersecurity training and awareness programs
- Include evidence of regular security assessments and improvements
- Highlight any industry certifications or compliance achievements
5. Cyber Insurance Costs and Money-Saving Strategies
Understanding cyber insurance for small business pricing helps you budget appropriately and identify opportunities to reduce premiums without sacrificing essential protection.
5.1 Average Cyber Insurance Costs by Business Type
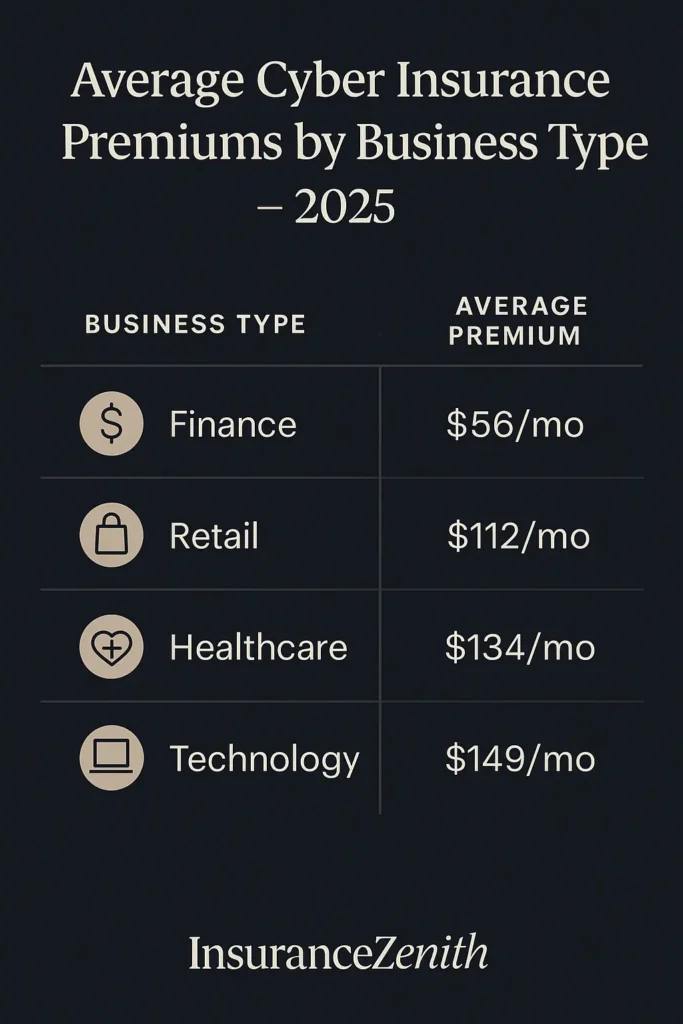
Cyber insurance for small business premiums vary significantly based on industry risk factors, business size, and security measures. Recent market analysis shows average monthly costs ranging from $56 to $149 depending on your business sector.
Industry-specific pricing breakdown:
- Financial services: $56/month average (lower risk due to regulatory compliance)
- Professional services: $89/month average (moderate risk profile)
- Retail businesses: $112/month average (customer payment data exposure)
- Healthcare providers: $134/month average (HIPAA compliance requirements)
- Technology companies: $149/month average (high-value targets)
Coverage limit pricing tiers:
| Coverage Amount | Small Business (1-10 employees) | Medium Business (11-50 employees) |
|---|---|---|
| $500,000 | $400-$800/year | $800-$1,200/year |
| $1,000,000 | $800-$1,500/year | $1,500-$2,500/year |
| $2,000,000 | $1,500-$2,800/year | $2,500-$4,500/year |
5.2 Factors That Influence Your Premium Costs
Insurance companies use sophisticated risk assessment models to price cyber insurance for small business policies. Understanding these factors helps you take steps to reduce your premiums.
Primary cost determinants:
- Annual revenue and number of employees
- Types and volume of sensitive data handled
- Industry sector and regulatory requirements
- Current cybersecurity measures and controls
- Claims history and previous security incidents
- Geographic location and state compliance requirements
Security measures that reduce premiums:
- Implementation of all five core security controls
- Regular employee cybersecurity training programs
- Documented incident response and recovery procedures
- Third-party security assessments and certifications
- Cyber liability coverage bundled with existing business policies
Businesses looking to reduce overall insurance costs should also explore our small business insurance cost analysis for comprehensive savings strategies.
5.3 Proven Strategies to Lower Cyber Insurance Premiums
Smart small business owners can significantly reduce cyber insurance for small business costs by implementing proper security measures and working with experienced insurance providers.
Immediate cost reduction opportunities:
- Bundle cyber coverage with existing business owner’s policy
- Increase deductibles to lower monthly premium payments
- Complete cybersecurity training for all employees before applying
- Implement multi-factor authentication across all business systems
- Establish automated backup procedures with regular testing
Long-term premium reduction strategies:
- Maintain clean claims history by preventing security incidents
- Regularly update and improve cybersecurity measures
- Work with cybersecurity consultants for ongoing assessments
- Participate in industry-specific security certification programs
- Document all security improvements and share with insurance providers
Our business insurance basics guide provides additional strategies for managing commercial insurance costs across all coverage types.
Conclusion: Protecting Your Business Future with Smart Cyber Insurance Decisions
Cyber insurance for small business has evolved from optional coverage to essential protection in 2025’s threat landscape. With cyber criminals specifically targeting smaller companies and attack costs averaging over $500,000 in total recovery expenses, the question isn’t whether you can afford cyber insurance—it’s whether you can survive without it.
Key takeaways for smart business owners:
- Cyber attacks will continue targeting small businesses at accelerating rates
- Basic data breach coverage costs $400-$800 annually for most small businesses
- Comprehensive cyber liability protection averages $145 monthly across all industries
- Proper security measures can reduce premiums by 20-40% while improving protection
Action steps to secure your business:
- Complete an honest assessment of your current cyber risks and vulnerabilities
- Research providers specializing in cyber insurance for small business coverage
- Implement the five core security controls before submitting applications
- Compare quotes from at least three providers to ensure competitive pricing
- Review and update your coverage annually as your business grows
Remember that cyber insurance works best as part of a comprehensive risk management strategy. The coverage provides crucial financial protection, but it cannot prevent attacks or instantly restore customer confidence after a breach.
For complete business protection, cyber insurance for small business should complement your existing commercial policies including general liability, professional liability, and business interruption coverage. This integrated approach ensures you’re protected against the full spectrum of business risks in today’s digital economy.
Disclaimers
This information is educational only and does not constitute insurance advice. Coverage needs vary by individual circumstances. Consult licensed insurance professionals for personalized recommendations.