Understanding health insurance claims and reimbursement processes is crucial for maximizing your healthcare benefits and minimizing out-of-pocket expenses. Whether you’re dealing with a routine medical visit or an emergency hospitalization, knowing how to navigate claims can save you thousands of dollars and reduce administrative headaches.
On This Page
In the next section, we’ll explore the fundamental concepts that form the backbone of all health insurance claims processing.
Essential Overview — What You Need to Know
A health insurance claim is a formal request by a healthcare provider to an insurance company for payment of medical services provided to a patient. The claims process involves multiple stakeholders: you as the patient, your healthcare provider, and your insurance company working together to ensure proper payment for covered medical services.
Key Takeaway: Most health insurance claims are filed automatically by your healthcare provider, but understanding the process helps you identify issues, appeal denials, and maximize your benefits. Similar to how life insurance beneficiary rules require proper documentation, health claims also depend on accurate paperwork and timely submission.
There are two primary types of health insurance claims:
- Cashless Claims: This type of claim facility allows you to receive cashless treatment at a network hospital, where the insurer pays the hospital directly
- Reimbursement Claims: You pay upfront for medical services and later request reimbursement from your insurer
How Claims Processing Works

Typically, your doctor’s office will submit a claim and you will not need to be involved in the process. The basic flow includes:
| Step | Process | Timeframe |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Service Delivery | Healthcare provider treats patient | Same day |
| 2. Claim Submission | Provider submits claim to insurer | Within 30 days |
| 3. Claim Review | Insurance company processes and evaluates | 15-30 days |
| 4. Payment/Denial | Insurer pays provider or denies claim | Within processing period |
Common Health Insurance Claims and Reimbursement Scenarios
Understanding when and how different claim types apply helps you make informed decisions about your healthcare. Just like choosing between term vs whole life insurance pros and cons, selecting the right claim approach depends on your specific situation and needs.
In the next section, we’ll dive deeper into exactly how the reimbursement process works step-by-step.
How Does Reimbursement Work in Health Insurance
Health insurance reimbursement involves your insurance company paying back expenses you’ve already covered for eligible medical services. A reimbursement claim is a formal request made by a policyholder to their health insurance provider, asking for a refund or compensation for out-of-pocket medical expenses incurred.
When Reimbursement Claims Are Necessary
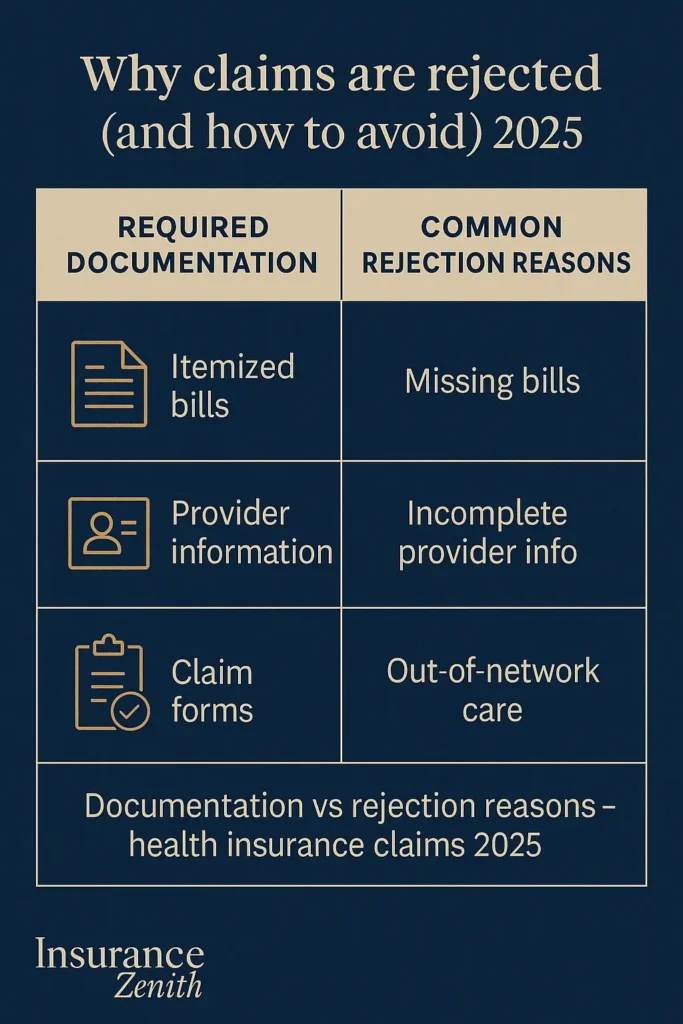
You typically need to file a reimbursement claim when:
• Out-of-network care: You receive treatment from providers not in your insurance network • Emergency situations: You need immediate care at non-network facilities
• Provider billing practices: Some providers require upfront payment before billing insurance • Cashless claim rejection: When pre-authorization is denied or unavailable • Travel-related medical care: Receiving treatment while away from your home area
Reimbursement Process Steps
Step 1: Pay for Services Initial payment of medical bills falls on the policyholder, with reimbursement typically occurring after the claim undergoes processing.
Step 2: Collect Documentation Gather essential documents including:
- Itemized medical bills
- Receipts for all payments
- Medical reports and discharge summaries
- Provider tax identification numbers
- Your insurance policy information
Step 3: Submit Claim You have to submit the required documents within 15 days of getting discharged from the hospital for most insurers.
Step 4: Await Processing This process may take around 21 days for standard reimbursement claims.
Key Takeaway: Reimbursement claims offer flexibility in provider choice but require upfront payment and longer processing times compared to cashless claims. Understanding health insurance open enrollment deadlines ensures you have proper coverage before needing to file any claims.
What Is the Reimbursement Process for Health Insurance
The reimbursement process varies depending on your specific insurance plan and the type of medical service received. Post-service claims are all other claims for benefits under your group health plan, including claims after medical services have been provided, such as requests for reimbursement or payment for the provided services.
Federal Requirements for Claim Processing

Under federal law (ERISA), insurance plans must meet specific timeframes:
| Claim Type | Decision Timeframe | Extension Allowed |
|---|---|---|
| Urgent care claims | 72 hours maximum | No extensions |
| Pre-service claims | 15 days | 15 additional days if needed |
| Post-service claims | 30 days | 15 additional days if needed |
Important: Plans are required to pay or provide benefits within a reasonable time after a claim is approved, though ERISA does not specify a time limit.
Documentation Requirements for Reimbursement
When filing a reimbursement claim yourself, ensure your claim gets processed smoothly with these essential documents:
- Completed claim form: Patient Request for Medical Payment form or your insurer’s specific form
- Itemized bills: Detailed invoices showing services provided, dates, and charges
- Proof of payment: Receipts, canceled checks, or credit card statements
- Medical records: When requested by the insurer for complex procedures
- Provider information: Complete details including tax ID and license numbers
Common Reimbursement Scenarios
Scenario 1: Emergency Care If you visit a non-network hospital for emergency treatment, you pay the bills upfront and collect the required documents. To get the reimbursement, you submit the claim and attach the required documents. Your medical expenses will be reimbursed after approval.
Scenario 2: Specialist Consultation When seeing an out-of-network specialist, you typically pay at the time of service and then submit reimbursement paperwork to recover covered expenses under your plan’s out-of-network benefits.
What Are the Three Common Types of Reimbursement
Health insurance reimbursement operates through three primary methodologies, each serving different healthcare delivery models and patient needs.
1. Fee-for-Service Reimbursement
This traditional model reimburses healthcare providers for each individual service performed. Under fee-for-service:
• Providers bill separately for each procedure, test, or consultation • Patients typically have maximum flexibility in provider choice • Insurance companies review each service for medical necessity and coverage • Reimbursement rates are predetermined through fee schedules
Key Features:
- Individual service billing
- No bundled payments
- Immediate reimbursement processing
- Higher administrative costs
2. Capitation-Based Reimbursement
Under capitation, insurance companies pay healthcare providers a fixed amount per member per month, regardless of services used. This model is common in Health Maintenance Organization (HMO) plans.
Characteristics:
- Fixed monthly payments to providers
- Providers manage all covered services within the capitation rate
- Incentivizes preventive care and cost management
- Limited to network providers
3. Value-Based Reimbursement
This emerging model ties reimbursement to patient outcomes and quality metrics rather than volume of services. In a value-based care model, length of stay and 30-day readmissions impact provider reimbursements.
Components:
- Quality performance metrics
- Patient satisfaction scores
- Cost-effectiveness measures
- Bundled payments for episodes of care
Health Insurance Claims and Reimbursement Timeframes
Understanding the complexity of health insurance claims and reimbursement processes helps you prepare for different scenarios. Similar to understanding pre-existing conditions coverage requirements, knowing your claim options prevents unexpected financial burdens.
Key Takeaway: The reimbursement method affects your out-of-pocket costs, provider options, and claim processing procedures, making it important to understand which model your plan uses.
In our next section, we’ll examine exactly how insurance companies evaluate and process your claims.
How Does Insurance Claim Reimbursement Work
Insurance claim reimbursement follows a systematic process designed to verify coverage, validate services, and ensure proper payment. The payor evaluates the claim, then decides whether the medical claim is valid and how much of the claim they will reimburse.
The Claims Adjudication Process
Step 1: Claim Submission Healthcare providers submit claims electronically using standardized forms containing:
- Patient demographic information
- Diagnosis codes (ICD-10)
- Procedure codes (CPT/HCPCS)
- Service dates and provider details
Step 2: Initial Processing Claims processors check the submission for:
- Completeness and accuracy
- Policy coverage verification
- Service date validity
- Provider network status
Step 3: Medical Review Complex claims undergo medical necessity review where:
- Licensed medical professionals evaluate treatment appropriateness
- Prior authorization requirements are verified
- Coverage limitations are applied
Step 4: Adjudication Decision The insurance company determines:
- Covered services and amounts
- Patient responsibility (deductibles, copays, coinsurance)
- Provider reimbursement rates
- Any claim denials or partial payments
Coordination of Benefits (COB)
When you have multiple insurance plans, coordination of benefits determines payment order:
| Order | Plan Type | Responsibility |
|---|---|---|
| Primary | Usually employer-sponsored plan | Pays first according to policy terms |
| Secondary | Medicare, spouse’s plan, or secondary coverage | Pays remaining covered expenses |
The goal is to make sure that the combined payments of all plans do not exceed 100% of the total allowable expenses.
Electronic vs. Paper Claims Processing
Research from the University of Massachusetts Amherst shows that low-income patients experience greater financial burden from health insurance claim denials, highlighting the importance of understanding different processing methods:
Electronic Claims (EDI 837):
- Process in 15-30 days typically
- Lower error rates
- Automatic status updates
- Faster reimbursement
Paper Claims:
- Process in 30-45 days
- Higher rejection rates
- Manual handling required
- Slower payment cycles
Important: Most healthcare providers now submit electronic claims, which significantly reduces processing time and improves accuracy.
In the next section, we’ll explore the official regulations that govern these processes and your rights as a consumer.
Official Regulations and Standards
Health insurance claims and reimbursement operate under a complex framework of federal and state regulations designed to protect consumers and ensure fair practices.
Federal Regulatory Framework
ERISA (Employee Retirement Income Security Act) governs most employer-sponsored health plans and establishes:
- Specific timeframes for claim decisions
- Appeal rights for denied claims
- Disclosure requirements for plan administrators
- Fiduciary responsibilities for plan management
HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) provides:
- Privacy protections for health information in claims processing
- Standard electronic transaction formats
- Security requirements for claims data
Affordable Care Act (ACA) enhanced consumer protections by requiring:
- Coverage for essential health benefits
- Prohibition of pre-existing condition exclusions
- Out-of-pocket maximums for covered services
- External review processes for denied claims
State Insurance Regulation
State insurance commissioners regulate health insurance within their jurisdictions, including:
- Network adequacy standards
- Claims payment timeframes
- Consumer complaint resolution
- Market conduct examinations
How to verify applicable rules in your state: Contact your state’s Department of Insurance through the National Association of Insurance Commissioners (NAIC) member directory. Each state maintains specific requirements for claims processing, appeal procedures, and consumer protections.
| Regulatory Area | Federal Authority | State Authority |
|---|---|---|
| ERISA Plans | Department of Labor | Limited oversight |
| Individual Market | CMS/HHS | Primary regulation |
| Medicaid | CMS oversight | State administration |
| Insurance Companies | Limited federal role | Primary regulation |
Key Takeaway: While federal laws provide baseline protections, state regulations often offer additional consumer safeguards and specific procedural requirements that vary by location.
State Variations in Claims Processing
Health insurance claims processing varies significantly across states due to different regulatory approaches, market structures, and consumer protection laws.
State-by-State Regulatory Differences
| State | Regulator (DOI) | Key Claims Specifics | Official Link |
|---|---|---|---|
| California | California Department of Insurance | 30-day payment requirement for clean claims | insurance.ca.gov |
| Texas | Texas Department of Insurance | Prompt pay standards with interest penalties | tdi.texas.gov |
| New York | New York Department of Financial Services | Enhanced external review process | dfs.ny.gov |
| Florida | Florida Office of Insurance Regulation | Specific hurricane-related claim procedures | floir.com |
| Illinois | Illinois Department of Insurance | Mental health parity enforcement | insurance.illinois.gov |
| Pennsylvania | Pennsylvania Insurance Department | Balance billing protections | insurance.pa.gov |
| Ohio | Ohio Department of Insurance | Prescription drug formulary requirements | insurance.ohio.gov |
| Michigan | Michigan Department of Insurance | Auto insurance coordination rules | michigan.gov/difs |
| Georgia | Georgia Department of Insurance | Short-term plan regulations | oci.ga.gov |
| North Carolina | North Carolina Department of Insurance | Provider network adequacy standards | ncdoi.gov |
State-Specific Consumer Protections
Prompt Payment Laws: Most states require insurers to pay clean claims within specific timeframes, typically 30-45 days, with interest penalties for late payments.
Appeal Processes: While federal law requires internal appeals, states may mandate additional protections such as:
- Independent medical reviews
- Expedited appeal timelines
- Consumer assistance programs
Network Adequacy: States set different standards for provider network adequacy, affecting your access to in-network care and potential reimbursement scenarios.
Advanced Health Insurance Claims Factors & Future Outlook
The health insurance claims landscape continues evolving with technological advances, regulatory changes, and market innovations that could significantly impact reimbursement processes in coming years.
Emerging Technologies in Claims Processing
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning are increasingly being deployed to:
- Automate claims adjudication for routine services
- Identify potential fraud patterns
- Predict claim costs and utilization
- Streamline prior authorization decisions
Blockchain Technology shows promise for:
- Securing patient data during claims processing
- Creating immutable audit trails
- Enabling real-time benefit verification
- Reducing administrative costs
Regulatory Developments and Trends
According to recent discussions in Congress, several proposed changes could affect future claims processing:
Price Transparency Initiatives: Federal rules now require hospitals and insurers to disclose pricing information, which could lead to more informed consumer decisions and affect reimbursement negotiations.
No Surprises Act Implementation: This federal legislation, which took effect in 2022, continues to be refined through regulatory guidance, affecting how out-of-network emergency claims are processed and reimbursed.
Telehealth Expansion: Ongoing discussions suggest potential permanent expansion of telehealth coverage, which could streamline claims processing for remote consultations and digital health services.
Anticipated Changes for 2026 and Beyond
Based on current regulatory proposals and industry trends, it is anticipated that several developments may affect health insurance claims:
Enhanced Interoperability: Federal initiatives could require improved data sharing between providers and insurers, potentially reducing claim processing delays and improving accuracy.
Value-Based Care Growth: The shift toward value-based reimbursement models may continue expanding, affecting how claims are evaluated and paid.
Consumer-Directed Health Plans: Growth in high-deductible health plans paired with health savings accounts could change reimbursement patterns and patient responsibility.
🔋 Regulatory Disclaimer: The developments described above are under discussion and do not constitute binding obligations. Always verify current regulations with official government sources such as CMS.gov, the Department of Labor, and your state insurance department.
Important: According to current proposals being reviewed by federal agencies, changes to claims processing requirements could be implemented over the next few years, but specific timelines remain subject to regulatory review and stakeholder input.
Frequently Asked Questions
How long does it take to get reimbursed by health insurance?
Generally, it takes up to 30 days to receive reimbursement after your insurance company processes a claim. Each claim timeline varies, but many are processed within 14 business days. Processing time depends on the payment method, your bank, and whether all required information has been submitted.
What documents do I need for a health insurance reimbursement claim?
Essential documents include completed claim forms, itemized medical bills, proof of payment (receipts or credit card statements), and any supporting medical documentation. Some insurers may require specific forms or additional information based on the type of service.
Can I get reimbursed if I go to an out-of-network provider?
Yes, most health insurance plans provide out-of-network benefits, though you’ll typically pay higher out-of-pocket costs. You’ll need to pay upfront and submit reimbursement paperwork. Check your policy for specific out-of-network reimbursement rates and annual limits.
What happens if my health insurance claim is denied?
If a claim is denied, you have the right to appeal the decision. Every health insurance plan offers an appeals process that allows you to request a second review. The insurance company must provide written explanation of the denial reason and instructions for filing an appeal.
How do I track the status of my health insurance claim?
Most insurers provide online portals or mobile apps where you can check claim status. You can also call your insurer’s customer service line with your claim number. Many provide real-time updates on claim processing stages.
What’s the difference between a cashless claim and reimbursement claim?
Cashless claims allow you to receive treatment at network hospitals without upfront payment—the insurer pays the hospital directly. Reimbursement claims require you to pay upfront and later request refund from your insurer. Cashless is more convenient but limited to network providers.
Can I submit a reimbursement claim for prescription medications?
Yes, if you pay out-of-pocket for covered prescription drugs (such as when traveling or at non-network pharmacies), you can typically submit receipts for reimbursement. Include the prescription receipt, proof of payment, and sometimes a prescription copy.
Is there a time limit for submitting health insurance reimbursement claims?
Yes, most insurers require claims to be submitted within a specific timeframe, typically 90 days to one year from the service date. Medicare claims must be filed no later than 12 months after services were provided. Check your policy for exact deadlines.
Key Takeaways & Resources
Understanding health insurance claims and reimbursement processes empowers you to maximize your healthcare benefits while minimizing financial stress during medical emergencies or routine care.
Essential Action Steps
• Know your plan: Review your health insurance policy to understand coverage limits, network requirements, and reimbursement procedures • Keep detailed records: Maintain organized files of all medical bills, receipts, and correspondence with your insurer
• Submit claims promptly: File reimbursement requests within required timeframes to avoid claim denials • Understand your rights: Familiarize yourself with appeal processes and consumer protections in your state • Use network providers when possible: Cashless claims through network hospitals reduce administrative burden and out-of-pocket costs
Official Resources for Further Information
• National Association of Insurance Commissioners (NAIC): content.naic.org/consumer/health-insurance.htm – Consumer guides and state insurance department contacts • U.S. Department of Labor: dol.gov/agencies/ebsa – ERISA protections and employee benefit information • Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services: cms.gov – Federal health insurance regulations and Medicare claim information • Healthcare.gov: healthcare.gov – Marketplace plans and consumer assistance • State Insurance Departments: Contact your state’s insurance commissioner for local regulations and consumer protection services
Final Considerations
Key Takeaway: Proactive understanding of your health insurance claims process, combined with proper documentation and timely submission, ensures you receive maximum benefits and reimbursement under your policy while avoiding common pitfalls that lead to claim denials or delays.
The health insurance landscape continues evolving with new technologies and regulations designed to improve consumer experiences and reduce administrative costs. Staying informed about these changes helps you adapt your approach to claims management and take advantage of improved processes as they become available.
Remember that while this guide provides comprehensive information about health insurance claims and reimbursement, your specific policy terms and state regulations may include additional requirements or protections. Always consult your policy documents and contact your insurer directly for guidance on specific situations or complex claims.