Car insurance Michigan requirements caught Marcus, a Flint mechanic, completely off guard when a minor fender-bender exposed his three-month insurance lapse. What began as a simple rear-end collision escalated into a $1,200 fine, suspended license, and financial nightmare that could have been avoided with proper Michigan car insurance.
Michigan’s uninsured motorist rate dropped by more than 6% between 2020 and 2022, yet 19.6% of Michigan drivers still operate without coverage according to Insurance Research Council data. This combination of strict enforcement and remaining coverage gaps creates both opportunities and risks for drivers seeking affordable car insurance Michigan solutions.
Understanding Michigan’s unique no-fault system and finding affordable coverage requires navigating complex PIP options, geographic rate variations, and recent legislative changes. Michigan car insurance rates vary dramatically by location, with Detroit drivers paying over three times more than Ann Arbor residents for identical coverage. Our comprehensive analysis of car insurance calculator tools shows Michigan drivers can save significantly through strategic coverage selection.
This guide reveals seven proven strategies to reduce car insurance Michigan premiums while maintaining legal compliance, based on current 2025 data from state regulators and insurance providers.
On This Page
1. Understanding Michigan’s No-Fault System Requirements
1.1 Mandatory Coverage Components
Michigan law mandates three specific coverage types that distinguish it from traditional tort states:
Personal Injury Protection (PIP): Medical coverage regardless of fault, with six selectable limits ranging from $50,000 to unlimited. If a PIP medical option is not chosen by the insured, the unlimited PIP medical option is selected by default.
Property Protection Insurance (PPI): Fixed $1 million coverage for property damage you cause to others. This covers vehicles, buildings, and stationary objects.
Residual Bodily Injury/Property Damage Liability: Minimum $50,000/$100,000 for injuries and $10,000 for additional property damage beyond PIP limits.
1.2 Recent Legal Changes Impact
For policies issued or renewed after July 1, 2020, insurance companies are subject to specific overall statewide PIP medical coverage premium reductions:
- $50,000 PIP option: 45% average reduction
- $250,000 PIP option: 35% average reduction
- $500,000 PIP option: 20% average reduction
- Unlimited PIP option: 10% average reduction
These mandated reductions have created opportunities for substantial car insurance Michigan savings, particularly for drivers who previously carried unlimited PIP by default. Many Michigan drivers can now reduce their annual premiums by $1,500 or more while maintaining adequate protection.
1.3 Electronic Enforcement System
Michigan’s electronic verification system allows law enforcement to check insurance status instantly during traffic stops. More than 202,000 previously uninsured Michiganders purchased auto insurance before the amnesty period ended on January 1, 2022, demonstrating the system’s effectiveness in encouraging compliance.
2. PIP Coverage Selection Strategy
2.1 Six Available PIP Options
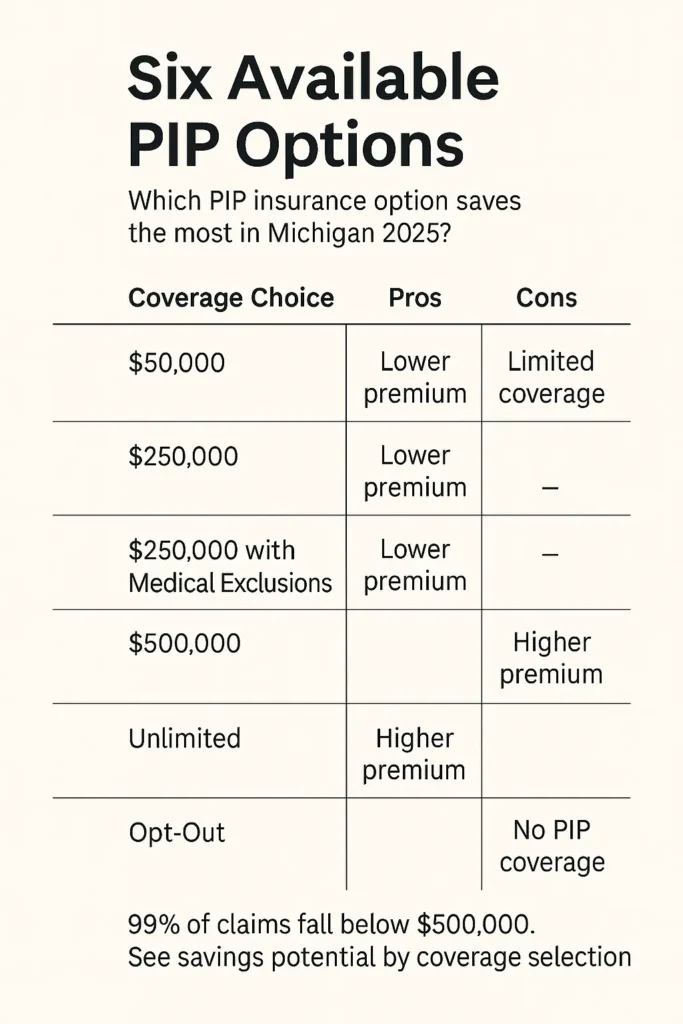
Michigan gives drivers the option to choose between six PIP medical coverage options based on their budget and insurance needs:
Unlimited Coverage: Pays all allowable medical expenses with no cap. Suitable for drivers without comprehensive health insurance or those prioritizing maximum protection.
$500,000 Limit: Reports show that 99% of all PIP claims have been covered with a $500,000 limit. Optimal balance for most drivers with adequate health coverage.
$250,000 Limit: Cost-effective for drivers with excellent health insurance that covers auto accident injuries. Requires careful evaluation of health plan exclusions.
$250,000 with Medical Exclusions: Available when household members have qualified health coverage. Reduces premiums by excluding covered individuals from PIP benefits.
$50,000 Limit: This option is only for drivers who are enrolled in Medicaid. Provides affordability for qualifying low-income drivers but carries significant financial risk for car insurance Michigan claims exceeding this amount.
PIP Opt-Out: Only named insureds with Medicare (Parts A and B) are eligible for this option. Requires all household members to have qualified health coverage.
2.2 Health Insurance Coordination
Selecting appropriate PIP levels requires understanding how your existing health coverage interacts with auto accident injuries. Many health plans exclude or limit coverage for motor vehicle accidents, making PIP your primary protection.
Critical evaluation factors include:
- Health insurance deductibles and out-of-pocket maximums
- Coverage exclusions for auto accident injuries
- Network restrictions for trauma and rehabilitation services
- Long-term care and attendant care benefits
2.3 Cost-Benefit Analysis
The Michigan Catastrophic Claims Association fee structure creates additional considerations. The MCCA fee for 2024-2025 is $90 per vehicle for unlimited PIP and $20 per vehicle for all other PIP options.
For comprehensive guidance on selecting appropriate coverage levels, explore our detailed analysis of how to calculate car insurance premium components. Understanding these calculation methods helps drivers make informed decisions about their Michigan car insurance coverage needs.
3. Geographic Rate Variations Across Michigan
3.1 City-by-City Premium Analysis
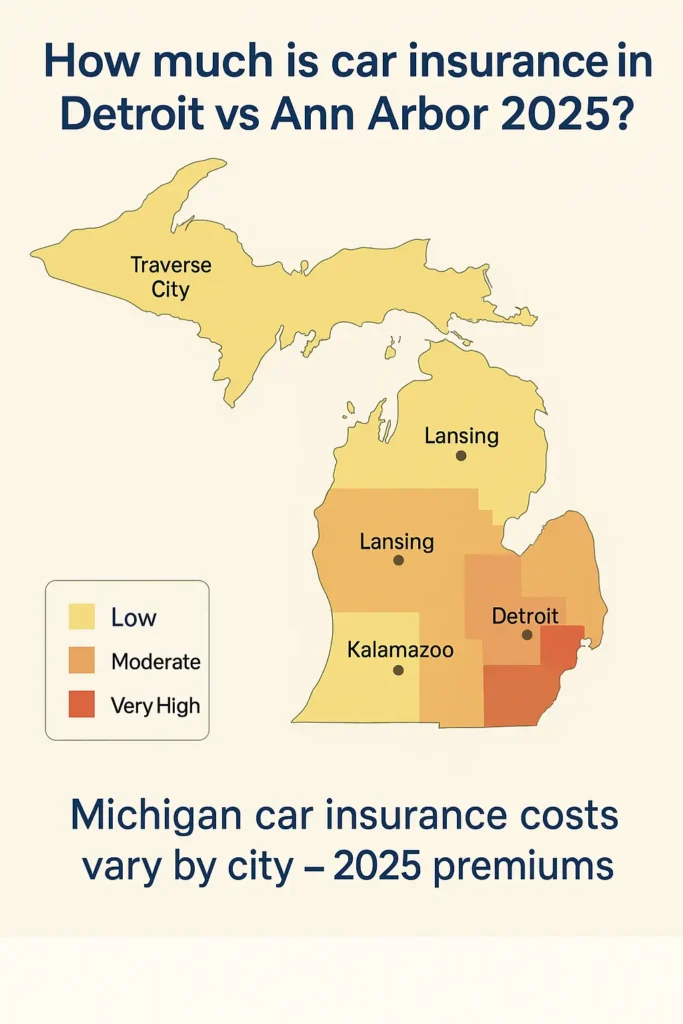
Michigan drivers pay an average monthly rate of $75 for minimum coverage and $270 for full coverage insurance, but location creates dramatic variations:
High-Cost Urban Areas:
- Detroit: $474 average monthly (full coverage)
- Flint: $325 average monthly
- Dearborn: $291 average monthly
Moderate-Cost Regional Centers:
- Grand Rapids: $178 average monthly
- Lansing: $195 average monthly
- Kalamazoo: $164 average monthly
Lower-Cost Areas:
- Ann Arbor: $133 average monthly
- Traverse City: $154 average monthly
- Marquette: $142 average monthly
3.2 Risk Factors Driving Regional Differences
Michigan’s uninsured driver rate of 20% is much higher than the national average of 14%, but this concentrates heavily in urban areas where at one point, 60% of Detroit drivers were thought to be uninsured.
Additional geographic factors include:
- Medical Cost Variations: Hospital and specialist pricing differs significantly between regions
- Litigation Frequency: Some metropolitan areas experience higher accident lawsuit rates
- Theft and Vandalism: Urban property crime rates affect comprehensive coverage costs
- Weather Patterns: Northern Michigan faces increased winter weather risks
3.3 Address Considerations
Using false addresses to obtain lower rates constitutes insurance fraud and results in claim denials. However, legitimate address changes for college students, seasonal residents, or relocating workers can create savings opportunities when properly disclosed to insurers.
4. Discount Optimization Strategies
4.1 Multi-Policy Bundling Benefits
Combining auto insurance with home or renters coverage typically generates 5-25% discounts while providing additional conveniences like unified claims handling and single renewal dates. Our comprehensive auto and renters insurance bundle analysis shows how Michigan drivers can maximize these multi-policy savings opportunities.
4.2 Driving Record Incentives
Safe driving discounts reward clean records over 3-5 year periods with reductions up to 40%. The 2019 auto insurance reform law prohibited auto insurance companies from using sex, marital status, home ownership, credit score, educational level and other non-driving factors in Michigan, making driving history more influential in rate determination.
4.3 Usage-Based Insurance Programs

Telematics programs monitor driving behaviors including speed, braking patterns, time of day, and phone usage while driving. Safe drivers can achieve discounts up to 30%, though aggressive or distracted drivers may face rate increases.
Key program features to evaluate:
- Monitoring period duration (typically 90 days)
- Specific behaviors tracked
- Maximum discount potential
- Rate increase limitations
- Privacy protections for collected data
4.4 Educational and Professional Discounts
Good student discounts apply to high school and college students maintaining 3.0+ GPAs, providing up to 20% savings. Some insurers also offer professional discounts for teachers, engineers, first responders, and military personnel.
5. Deductible and Coverage Limit Optimization
5.1 Deductible Selection Strategy
Raising comprehensive and collision deductibles from $250 to $1,000 can reduce premiums by 15-25%. This strategy works best when you maintain emergency savings equal to your deductible amount.
Deductible Selection Framework:
- $250-$500: Suitable for drivers with limited emergency funds
- $1,000: Optimal for most drivers with adequate savings
- $1,500-$2,500: Consider only with substantial emergency reserves
5.2 Liability Limit Adjustments
While Michigan requires minimum $50,000/$100,000 bodily injury coverage, BI coverage will default to $250,000/$500,000 under the new law, but consumers may choose lower limits by completing a selection form.
Medical expenses from severe accidents easily exceed minimum limits, making higher coverage financially prudent despite increased premiums.
5.3 Uninsured Motorist Protection
With Michigan having 19.6% uninsured drivers, uninsured motorist coverage protects against accidents with drivers lacking proper insurance. While not required, this coverage fills important gaps in Michigan’s no-fault system.
6. Insurer Selection and Shopping Strategy
6.1 Market Competition Analysis
The reform law has increased competition by encouraging new companies and affiliates to enter the Michigan market. This expanded competition creates more options and potential savings for consumers.
Regional vs. National Insurer Considerations:
- Regional Insurers: Often provide better local service and competitive rates for specific areas
- National Companies: Typically offer more technological conveniences and broader network services
- Direct Writers: May provide lower rates by eliminating agent commissions
- Independent Agents: Offer comparison shopping across multiple insurers
6.2 Quote Comparison Methodology
Effective comparison requires identical coverage specifications across all quotes:
- Same PIP level selection
- Identical deductible amounts
- Matching liability limits
- Consistent optional coverage selections
6.3 Financial Stability Assessment
Verify insurer financial strength through A.M. Best ratings, focusing on companies rated A- or higher. Lower-rated insurers may offer attractive rates but could struggle with claim payments during financial stress periods.
For comprehensive insurer evaluation tools, review our analysis of cheap car insurance in Colorado which demonstrates comparison methodologies and shows how car insurance Michigan pricing compares to other states with similar demographics.
7. Avoiding Common Coverage Mistakes
7.1 PIP Level Misalignment
Choosing PIP coverage without evaluating existing health insurance creates either dangerous gaps or expensive redundancies. If you choose a lower level of PIP medical coverage and you don’t have health insurance, you may be personally responsible for your medical costs that exceed your PIP medical coverage limit.
7.2 Minimum Liability Risks
State minimum liability coverage rarely provides adequate protection against serious accident lawsuits. Average Claim Costs: Michigan insurers pay roughly $555,000 per person for lifetime medical care under PIP claims, indicating the potential magnitude of liability exposure.
7.3 Gap Coverage Oversights
Leased and financed vehicles require gap insurance to cover depreciation differences between loan balances and actual cash values. Standard liability and collision coverage don’t address this exposure, leaving drivers potentially responsible for thousands in remaining loan balances after total loss incidents.
7.4 Documentation and Compliance
Maintaining current proof of insurance prevents unnecessary violations during traffic stops. Michigan’s electronic verification system reduces but doesn’t eliminate the need for proper documentation, particularly when driving out of state.
Legal Consequences of Non-Compliance
8.1 Immediate Penalties
Michigan enforces uninsured driving violations consistently:
- First Offense: $500 fine, 30-day license suspension, $250 reinstatement fee
- Repeat Violations: Misdemeanor charges, extended suspensions up to one year
- SR-22 Requirements: Mandatory high-risk insurance certificates costing $1,200+ annually
8.2 Long-Term Financial Impact
License suspension creates cascading problems including employment difficulties, increased insurance costs after reinstatement, and limited insurer options. These consequences often exceed the cost of maintaining continuous coverage.
8.3 Civil Liability Exposure
Uninsured drivers bear full financial responsibility for accident costs, including medical expenses, property damage, legal fees, and lost wages. Even minor accidents can result in claims exceeding $50,000, creating long-term financial obligations.
The Michigan Department of Insurance and Financial Services provides official guidance and rate comparison tools at michigan.gov/difs for consumers seeking regulatory information and complaint procedures.
Premium Calculation Factors
9.1 Driver-Specific Variables
Your driving record, age, and location affect your rates, with accidents, violations and younger drivers facing higher costs. The 2019 reform eliminated several rating factors while maintaining others:
Prohibited Factors (Cannot Be Used):
- Gender and marital status
- Credit scores and educational level
- Home ownership and occupation
- ZIP code (with limited exceptions)
Permitted Factors (Still Used):
- Driving record and claim history
- Age and licensed driver experience
- Vehicle type and safety features
- Annual mileage and usage patterns
- Coverage selections and deductible choices
9.2 Vehicle-Related Considerations
Vehicle type can play a significant role in Michigan rates, with drivers of a BMW 330i paying an average of 37 percent more for insurance per year than someone driving a Ford F-150.
Factors affecting vehicle-based pricing:
- Theft susceptibility: Higher-theft vehicles increase comprehensive costs
- Repair expenses: Luxury and imported vehicles cost more to repair
- Safety ratings: Vehicles with better crash test scores may qualify for discounts
- Age and depreciation: Older vehicles may not require comprehensive/collision coverage
9.3 Usage Pattern Impact
Your car type, coverage amounts, credit score, and annual mileage also impact premiums. Low-mileage discounts benefit drivers with annual usage under 7,500 miles, while high-mileage drivers face increased rates reflecting higher accident exposure.
Insurance Fraud Prevention
9.1 Current Fraud Landscape
The Michigan Department of Insurance and Financial Services (DIFS) Fraud Investigation Unit received 3,789 fraud reports between July 1, 2023, and June 30, 2024. Alarmingly, 99% of these reports were insurance-related, with 50% involving auto and no-fault claims.
9.2 Common Fraud Schemes
Michigan’s no-fault system creates particular vulnerabilities to medical provider fraud, staged accidents, and inflated claims. These fraudulent activities increase costs for all drivers through higher premiums and reduced insurer competition.
9.3 Consumer Protection Measures
The state’s fraud prevention efforts include provider fee schedules, utilization reviews, and enhanced investigative capabilities. The new law establishes a fee schedule between auto insurers and medical providers designed to control the costs that medical providers may charge auto insurers for their services. Understanding these fraud prevention measures helps Michigan car insurance consumers recognize legitimate savings versus deceptive schemes.
Conclusion: Optimizing Your Michigan Auto Insurance
Car insurance Michigan requirements present both challenges and opportunities for cost-conscious drivers. Strategic PIP selection based on existing health coverage, geographic considerations, and comprehensive discount utilization can generate savings of $1,800 or more annually while maintaining legal compliance.
The 2019 reform created unprecedented flexibility in coverage selection, but this freedom requires informed decision-making to avoid dangerous coverage gaps. Understanding the interplay between PIP options, health insurance coordination, and liability protection ensures adequate protection without overpaying.
Key optimization strategies include:
- Selecting PIP levels that complement rather than duplicate existing health coverage
- Leveraging geographic rate differences through legitimate address considerations
- Maximizing available discounts through safe driving, bundling, and usage-based programs
- Maintaining adequate liability limits despite minimum requirement temptations
- Shopping annually with multiple insurers to capture competitive rate changes
Michigan experienced the largest decrease of any state in the nation in its uninsured motorist rate following reform implementation, demonstrating that affordable coverage options can successfully increase compliance when properly structured.
For ongoing updates on Michigan insurance regulations and additional cost-saving strategies, explore Insurance Zenith’s comprehensive guides including cheap car insurance in Texas for multi-state comparisons and liability vs full coverage car insurance to understand Michigan’s coverage requirements in context.
Frequently Asked Questions
Who is the cheapest car insurance in Michigan?
Regional insurers like Auto-Owners, Farm Bureau, and Frankenmuth often provide the most competitive rates in Michigan. However, the cheapest option varies significantly by location – what’s affordable in Grand Rapids may be expensive in Detroit. State Farm and GEICO also offer competitive rates for certain driver profiles.
What’s the average cost for car insurance in Michigan?
Michigan drivers pay an average of $270 per month for full coverage and $75 for minimum coverage. Annual costs average $3,236 for full coverage, though this varies dramatically by city – Detroit averages $5,700+ while Ann Arbor averages around $1,600.
Is $300 a month bad for insurance?
$300 monthly is above Michigan’s average but may be reasonable depending on your situation. In Detroit or Flint, $300 could indicate good value for comprehensive coverage. In smaller cities, this amount suggests you may benefit from shopping for better rates or adjusting coverage levels.
Who really has the cheapest insurance?
The truly cheapest insurance varies by individual circumstances, but consistently competitive companies in Michigan include Auto-Owners for regional coverage, GEICO for younger drivers, and State Farm for bundling discounts. The key is comparing identical coverage levels from multiple insurers annually.