Car insurance calculator tools can save you serious money, but most drivers don’t know how to use them effectively. Tired of paying premium rates without understanding why your neighbor gets quoted $600 less for identical coverage? You’re not alone—thousands of Americans overpay simply because they don’t understand how insurance pricing actually works.
Here’s the reality: car insurance calculator algorithms evaluate dozens of hidden variables that dramatically impact your final premium. Your age, ZIP code, credit score, and even your vehicle’s specific trim level create pricing variations of 200-300% between similar drivers. The average American now spends $1,127 annually on auto insurance according to the National Association of Insurance Commissioners, but smart calculator users consistently pay 20-40% below these averages.
Critical Discovery: Car insurance calculator accuracy varies wildly between platforms. Some provide ballpark estimates while others access real-time underwriting databases. Understanding these differences prevents costly surprises and helps you identify genuine savings opportunities before committing to policies.
What most people miss is that car insurance calculator tools serve dual purposes—premium estimation and education about risk factors you can actually control. Smart users discover which variables create the biggest financial impact and adjust accordingly. You might learn that moving five miles affects your premium more than switching vehicles, or that improving your credit score saves more than raising your deductible.
Money-Saving Reality Check: Drivers who properly utilize multiple car insurance calculator platforms before shopping typically save $300-800 annually compared to those who accept the first quote they receive.
This guide reveals exactly how car insurance calculator systems work behind the scenes, which factors create the largest premium swings, and how to strategically use these tools to minimize your costs while maximizing protection. Whether you’re buying your first policy or reviewing existing coverage, understanding calculator mechanics puts you in control of your insurance budget.
On This Page
1. Car Insurance Calculator Technology and Risk Assessment Methods
Car insurance calculator platforms utilize sophisticated risk modeling algorithms that analyze hundreds of data points to predict claim probability and determine appropriate premium pricing for individual drivers and vehicles.
Modern Calculator Infrastructure:
- Real-Time Database Integration: MVR records, credit reports, and claims history verification
- Actuarial Analysis Systems: Statistical modeling based on millions of historical claims
- Geographic Risk Mapping: ZIP code-specific crime, weather, and accident frequency data
- Vehicle Valuation Networks: Real-time market pricing and safety rating integration
- Regulatory Compliance Engines: State-specific requirement and pricing rule enforcement
1.1 Understanding Car Insurance Calculator Risk Algorithms
Car insurance calculator systems employ predictive modeling that correlates personal characteristics with statistical claim patterns to determine individual risk classifications and appropriate pricing tiers.
Primary Risk Calculation Factors: Insurance companies analyze demographic data because specific groups demonstrate measurably different claim patterns. According to Insurance Information Institute research, drivers aged 16-24 file claims at rates 67% higher than experienced drivers aged 30-50. This statistical reality drives age-based pricing multipliers that can double or triple premiums for young drivers.
Geographic risk assessment plays an equally crucial role in car insurance calculator algorithms. Urban drivers face claim rates 40% higher than rural counterparts due to traffic density, theft probability, and accident frequency variations. Calculator systems divide regions into rating territories based on historical loss data, with neighboring ZIP codes sometimes showing dramatic premium differences.
Credit-Based Insurance Scoring: Most car insurance calculator platforms incorporate credit-based insurance scores where legally permitted. NAIC research demonstrates that drivers with poor credit file claims 40% more frequently than those with excellent credit. However, seven states—California, Hawaii, Massachusetts, Michigan, Montana, North Carolina, and Pennsylvania—prohibit or restrict credit score usage in premium calculations.
1.2 Vehicle-Specific Car Insurance Calculator Analysis
Car insurance calculator tools evaluate vehicle characteristics through comprehensive databases that assess safety performance, theft probability, and repair cost projections for accurate premium calculations.
Safety Rating Integration: Calculator algorithms access IIHS (Insurance Institute for Highway Safety) and NHTSA crash test databases to apply safety-based discounts or surcharges. Vehicles earning Top Safety Pick awards typically qualify for 5-15% premium reductions, while cars with poor crash ratings face corresponding increases.
Theft and Loss Data Processing: Car insurance calculator systems reference National Insurance Crime Bureau statistics to identify high-theft vehicles. Popular targets like certain Honda Civic and Toyota Camry model years may face 10-25% higher comprehensive coverage costs compared to vehicles with advanced anti-theft systems.
Repair Cost Analysis: Calculator platforms analyze average repair costs using industry databases that track parts pricing, labor rates, and complexity factors. Luxury vehicles with expensive components and specialized repair requirements generate higher collision coverage premiums compared to mainstream models with readily available, affordable parts.
1.3 Real-Time Premium Calculation Processing
Advanced car insurance calculator platforms provide instant estimates by accessing multiple data sources simultaneously while applying carrier-specific underwriting guidelines for accurate pricing projections.
Database Query Coordination: Modern calculator systems perform real-time verification checks against MVR databases, CLUE reports, and credit agencies to ensure accurate risk assessment. This comprehensive approach provides estimates within 5-10% of final underwritten premiums, significantly improving reliability compared to simplified estimation tools.
State Regulatory Compliance: Car insurance calculator algorithms automatically adjust for state-specific requirements and pricing regulations. For example, no-fault states like Michigan require Personal Injury Protection coverage, while others mandate uninsured motorist protection. Calculator systems incorporate these mandatory coverages to provide legally compliant estimates.
For comprehensive understanding of how these sophisticated systems process your information, exploring detailed analysis of how to calculate car insurance premium methodologies provides additional insights into the mathematical foundations underlying modern insurance pricing technology.
2. Critical Factors That Drive Car Insurance Calculator Results
Car insurance calculator outcomes depend heavily on specific personal and vehicle characteristics that create measurable differences in claim probability and cost exposure for insurance companies.
2.1 Age and Gender Impact on Car Insurance Calculator Pricing
Demographic factors significantly influence car insurance calculator results due to well-documented statistical correlations between age groups, gender categories, and actual claim frequencies across the insurance industry.
Age-Based Risk Multipliers: Car insurance calculator algorithms apply substantial age-based adjustments reflecting real claim data. According to Experian’s 2025 analysis, 18-year-old drivers pay an average of $3,608 annually compared to drivers in their 50s who pay $2,008 annually—nearly 80% more for identical coverage. These dramatic differences reflect statistical evidence that young drivers cause accidents at much higher rates.
Teen Driver Premium Calculations: The most significant car insurance calculator adjustments occur for drivers under 25. Males aged 16-19 face the highest premiums due to CDC research showing fatal crash rates three times higher than female drivers of identical ages. Calculator systems typically assign risk multipliers of 2.5-4.0x base rates for teen drivers, with young males receiving the highest classifications.
Gender-Based Pricing Considerations: In states permitting gender-based pricing, car insurance calculator tools apply different rates reflecting statistical accident patterns. Men drive more miles annually and engage more frequently in risky behaviors like speeding or driving under influence, according to IIHS research. However, seven states now prohibit gender considerations in premium calculations.
2.2 Credit Score and Financial Factors in Car Insurance Calculator Systems
Credit-based insurance scoring represents one of the most significant variables in car insurance calculator algorithms, where legally permitted, due to strong correlations between financial responsibility and claim frequency.
Credit Score Impact Analysis: Bankrate’s 2023 research reveals that drivers with poor credit pay 104% more for full coverage compared to those with excellent credit scores. Car insurance calculator systems in permissible states access credit-based insurance scores (different from regular credit scores) to assess financial risk patterns that correlate with claim behaviors.
State-by-State Credit Usage: Car insurance calculator platforms automatically adjust for state regulations regarding credit score usage. California, Hawaii, Massachusetts, and Michigan prohibit or severely limit credit-based pricing, requiring calculator algorithms to rely more heavily on driving records and other risk factors.
Credit Improvement Benefits: The financial impact of credit improvements can be substantial in calculator results. Improving credit from poor to good categories may reduce premiums by $500-1,500 annually, making credit repair one of the most cost-effective ways to lower insurance costs where legally applicable.
2.3 Geographic Location Effects on Car Insurance Calculator Estimates
Geographic factors create some of the largest variations in car insurance calculator results, with location-based risk assessments sometimes tripling premiums between neighboring areas.
ZIP Code-Specific Pricing: Car insurance calculator systems divide geographic areas into rating territories based on historical claim patterns. Urban drivers consistently face higher premiums—up to 214% more according to MoneyGeek analysis—due to increased accident frequency, theft rates, and vandalism probability compared to rural areas.
State Regulatory Environment Impact: Each state’s insurance regulations dramatically affect car insurance calculator results. Michigan’s unlimited Personal Injury Protection requirements create significantly higher premiums than neighboring states with more limited coverage mandates. Calculator systems automatically incorporate these state-specific requirements into pricing algorithms.
Weather and Natural Disaster Considerations: Car insurance calculator platforms factor regional weather patterns and natural disaster frequency into comprehensive coverage pricing. Areas prone to hail, flooding, or hurricane damage show higher comprehensive premiums reflecting increased claim probability and repair costs.
Understanding how these multiple factors interact within factors that affect car insurance rates provides deeper insights into optimizing your personal risk profile for better calculator results and lower premium costs.
3. Step-by-Step Car Insurance Calculator Optimization Strategy
Maximizing car insurance calculator accuracy and value requires systematic preparation, strategic information entry, and comprehensive results analysis to identify the best coverage options and pricing opportunities.
3.1 Pre-Calculator Information Gathering and Documentation
Successful car insurance calculator sessions begin with comprehensive documentation preparation that ensures accurate estimates and prevents costly errors during the underwriting process.
Essential Personal Documentation:
- Driver’s License Details: Complete license number, issue date, expiration, and any restrictions or endorsements
- Social Security Information: Required for credit checks and identity verification in most calculator systems
- Employment Verification: Current occupation, employer details, and income range affecting risk classification
- Educational Background: Degree completion data that may qualify for educational discounts
Complete Vehicle Information Package:
- Vehicle Identification Number (VIN): Provides exact specifications, safety ratings, and theft probability data
- Registration Documentation: Current registration status, title information, and lien holder details
- Purchase Information: Acquisition date, price paid, and current estimated value for coverage calculations
- Annual Mileage Estimation: Accurate driving patterns significantly impact premium calculations
Comprehensive Driving History Assembly:
- Motor Vehicle Record (MVR): Official report from state DMV showing violations, accidents, and license status
- Claims History Documentation: Previous insurance claims within 5-7 years affecting risk assessment
- Continuous Coverage Records: Proof of prior insurance preventing gaps that increase premiums
3.2 Strategic Information Entry for Maximum Car Insurance Calculator Accuracy
Car insurance calculator platforms require specific information entry techniques to generate the most accurate estimates and avoid discrepancies during final underwriting review.
Demographic Information Precision: Enter personal details exactly as they appear on official documents to prevent verification delays. Minor variations in name spelling, address formatting, or birth date entry can trigger additional review processes that slow quote generation and potentially affect final pricing.
Driving Record Transparency: Include all traffic violations, accidents, and claims within the calculator’s specified timeframe, typically 3-5 years. Attempting to conceal negative information invariably surfaces during underwriting and can result in policy cancellation or claim denials. Honest disclosure enables accurate calculator results and prevents unpleasant surprises.
Vehicle Details Optimization: Use your exact VIN when available rather than generic make/model selections. VIN-specific data provides precise safety ratings, theft statistics, and repair cost information that can favorably impact calculator results for well-equipped or highly-rated vehicles.
3.3 Advanced Car Insurance Calculator Results Analysis and Comparison
Comprehensive car insurance calculator results analysis involves examining both total costs and individual coverage components to identify optimization opportunities and ensure adequate protection.
Premium Breakdown Examination: Review calculator results by analyzing individual coverage costs—liability, collision, comprehensive, and additional protections. Understanding how much you pay for each component reveals opportunities for deductible adjustments, coverage limit modifications, or elimination of unnecessary protections.
Multi-Platform Comparison Strategy: Use car insurance calculator tools from 3-5 different providers to identify pricing patterns and coverage variations. Significant premium differences for identical coverage often indicate different risk assessment methodologies or target market preferences among insurers.
Coverage Adequacy Assessment Framework: Car insurance calculator platforms enable scenario modeling with different coverage levels and deductibles. Experiment with various combinations to understand financial tradeoffs—higher deductibles reduce premiums but increase out-of-pocket costs during claims.
Long-Term Cost Projection Analysis: Consider how calculator results might change over time due to aging, claims experience, or life changes. Some platforms provide multi-year projections that help evaluate long-term value propositions among different carriers and coverage options.
For comprehensive guidance on translating calculator insights into actionable decisions, exploring detailed information about auto insurance estimate optimization strategies provides additional frameworks for maximizing both coverage value and cost efficiency across different calculator platforms.
4. Common Car Insurance Calculator Errors and Prevention Strategies
Car insurance calculator mistakes can lead to significant premium discrepancies, coverage gaps, or unexpected costs during the actual underwriting process, making error prevention crucial for accurate decision-making.
4.1 Information Accuracy Problems and Their Financial Consequences
The most frequent car insurance calculator errors stem from incomplete or incorrect data entry, creating unrealistic expectations about final premium costs and potentially compromising coverage adequacy.
Mileage Misrepresentation Impacts: Many drivers underestimate annual mileage by 20-40% to obtain lower car insurance calculator quotes. However, insurance companies verify mileage through odometer readings, telematics programs, and claims investigations. Misrepresenting annual driving creates two problems: artificially low calculator estimates and potential policy violations that can void coverage during claims.
Geographic Location Manipulation: Some users attempt to game car insurance calculator systems by using addresses in lower-risk areas—parents’ homes, friends’ addresses, or previous residences. This practice constitutes insurance fraud and creates substantial legal and financial risks. Your garaging address must accurately reflect where you park your vehicle overnight.
Driving Record Concealment Consequences: Failing to disclose traffic violations, accidents, or license suspensions in car insurance calculator tools creates false premium expectations. Insurance companies access comprehensive MVR databases during underwriting, and undisclosed incidents typically result in premium increases of 15-50% or policy cancellations.
4.2 Coverage Selection Misunderstandings in Car Insurance Calculator Tools
Car insurance calculator platforms often present coverage options without adequate education, leading to poor decisions about protection levels and financial exposure management.
Minimum Coverage Misconceptions: Many car insurance calculator users select state minimum requirements assuming adequate protection. However, minimum limits rarely cover serious accident costs. Texas requires only $30,000 bodily injury coverage per person, but average medical costs for severe injuries often exceed $100,000-200,000, leaving drivers financially exposed.
Deductible Selection Errors: High deductible choices dramatically reduce car insurance calculator premiums but create financial hardship during claims. Choose deductibles you can comfortably afford—typically 1-3% of annual income—without compromising your financial stability during emergencies.
Comprehensive vs. Collision Confusion: Car insurance calculator tools sometimes group these coverages together without explanation. Comprehensive protects against theft, vandalism, weather damage, and animal collisions, while collision covers accidents with vehicles or objects. Understanding these distinctions helps make informed decisions about coverage needs and budget allocation.
4.3 Platform Limitations and Market Timing Issues
Relying exclusively on car insurance calculator estimates without understanding their limitations can lead to poor provider selection and inadequate coverage planning.
Instant Quote Reliability Limitations: Quick car insurance calculator tools prioritize convenience over accuracy, often providing estimates that vary 15-30% from final underwritten premiums. These simplified algorithms may not account for carrier-specific underwriting guidelines, recent regulatory changes, or complex risk factors unique to individual situations.
Discount Application Inconsistencies: Car insurance calculator estimates frequently display maximum available discounts rather than realistic savings for specific situations. Actual discount eligibility requires verification of qualifying criteria—good student status, defensive driving completion, professional affiliations, or home ownership—that may not apply to all users.
Market Timing and Rate Volatility: Car insurance calculator results represent pricing at specific moments, but rates change frequently due to market conditions, regulatory updates, and carrier business strategies. The NAIC reports that average premiums increased 5.75% in 2022 alone, meaning calculator results generated months apart may show substantial differences for identical coverage.
Carrier Algorithm Differences: Each insurance company uses proprietary car insurance calculator algorithms that weight risk factors differently. A driver considered high-risk by one carrier’s calculator may receive standard rates from another due to different underwriting philosophies and target market strategies.
To avoid these common pitfalls while maximizing car insurance calculator effectiveness, focus on providing complete, accurate information, understanding coverage options thoroughly, and using calculator results as starting points for comprehensive insurance consultations rather than final purchase decisions.
5. Advanced Car Insurance Calculator Features and Optimization Tools
Modern car insurance calculator platforms offer sophisticated analytical capabilities beyond basic premium estimation, providing valuable insights for coverage optimization and long-term financial planning.
5.1 Scenario Modeling and Comparative Analysis Tools
Advanced car insurance calculator systems enable comprehensive scenario analysis, allowing users to model different coverage combinations and understand their financial implications across various risk situations.
Coverage Limit Impact Modeling: Sophisticated car insurance calculator platforms demonstrate how liability limit changes affect both costs and protection levels. Increasing bodily injury coverage from $100,000 to $300,000 per person typically adds only $12-20 monthly but provides significantly better lawsuit protection. Calculator tools help quantify this risk-versus-cost relationship.
Deductible Optimization Analysis: Advanced calculators analyze the mathematical relationship between deductible levels and premium savings over multiple years. These tools factor your driving history, vehicle value, and local claim frequencies to recommend optimal deductible selections that balance immediate costs with long-term financial efficiency.
Multi-Vehicle Household Modeling: Premium calculator platforms designed for families enable comprehensive household insurance planning. These systems reveal opportunities for multi-car discounts, driver assignment optimization, and coverage standardization that can generate savings of 15-25% compared to individual policy arrangements.
5.2 Risk Assessment and Prevention Integration
Premium car insurance calculator tools increasingly incorporate predictive risk assessment features that help users understand and potentially mitigate factors contributing to higher insurance costs.
Telematics Program Preview Capabilities: Some car insurance calculator platforms model potential savings from usage-based insurance programs by analyzing your driving patterns against program criteria. These tools help determine whether telematics programs like Progressive’s Snapshot or State Farm’s Drive Safe & Save might reduce premiums based on typical driving behaviors.
Credit Score Impact Projection: Advanced calculator systems demonstrate how credit score improvements affect insurance premiums in states permitting credit-based pricing. These tools show potential annual savings from credit score improvements, helping prioritize financial decisions that impact both insurance costs and overall financial health.
Vehicle Safety Rating Integration: Premium car insurance calculator platforms that integrate IIHS and NHTSA safety databases show how different vehicle choices affect insurance costs. These tools help car shoppers understand insurance implications before purchase decisions, potentially saving hundreds annually through strategic vehicle selection.
5.3 Long-Term Financial Planning and Cost Projection
The most sophisticated car insurance calculator platforms provide multi-year cost projections and comprehensive financial planning features supporting strategic insurance decision-making.
Claims Impact Modeling: Advanced calculators project how potential claims might affect premiums over 3-5 year periods, helping users understand long-term financial consequences of deductible selections and coverage choices. These tools factor accident forgiveness programs, claims-free discounts, and carrier-specific penalty structures.
Life Event Planning Integration: Premium calculation tools with life event modeling help users understand how major changes—marriage, home purchases, career transitions, or adding teen drivers—will affect insurance costs. This forward-looking analysis enables better financial planning and optimal timing of major decisions.
Carrier Performance Analysis: Sophisticated comparison tools analyze total cost of ownership across different insurance carriers, factoring initial savings, loyalty discounts, claims handling quality, and long-term rate stability. These comprehensive analyses help users make informed decisions about provider selection based on long-term value rather than initial premium savings.
Geographic Mobility Planning: Advanced car insurance calculator platforms enable users to model how relocating to different areas might affect insurance costs. These tools help with decision-making about job relocations, retirement planning, or educational choices by quantifying insurance cost implications of geographic changes.
For comprehensive understanding of how these advanced features integrate with overall insurance optimization strategies, exploring detailed information about car insurance quote analysis techniques provides additional insights into maximizing both coverage value and cost efficiency across different calculator platforms.
6. Choosing the Right Car Insurance Calculator Platform
Different car insurance calculator platforms serve varying purposes and user needs, from quick estimates to comprehensive insurance planning and comparison shopping tools that require careful evaluation and selection.
6.1 Platform Feature Analysis and Accuracy Assessment
The most effective car insurance calculator tools combine precision, comprehensiveness, and transparency while providing clear information about their data sources and calculation methodologies.
Data Integration Standards: Premium car insurance calculator platforms that access official databases—MVR records, credit agencies, and VIN databases—provide significantly more accurate estimates than tools relying solely on user-reported information. Look for calculators that specify their data sources and update frequencies to ensure current, reliable pricing information.
Educational Component Integration: Superior car insurance calculator tools include comprehensive educational features explaining coverage options, state requirements, and risk factors throughout the estimation process. These integrated learning components help users make informed decisions rather than simply generating price comparisons without context.
Mobile Optimization and User Experience: Modern car insurance calculator platforms should function seamlessly across all devices while maintaining full functionality. Mobile-optimized calculators enable convenient information gathering using smartphone cameras for document capture and provide saved progress capabilities for later review and comparison.
6.2 Single-Carrier vs. Multi-Carrier Car Insurance Calculator Comparison
Understanding the fundamental differences between proprietary carrier calculators and multi-carrier comparison platforms helps align tool selection with your shopping approach and comparison needs.
Single-Carrier Calculator Advantages: Insurance company proprietary car insurance calculator tools often provide the most accurate estimates for specific carriers because they utilize exact underwriting algorithms and real-time pricing systems. These platforms typically offer more detailed customization options and immediate quote binding capabilities with streamlined application processes.
Multi-Carrier Comparison Platform Benefits: Aggregation sites provide simultaneous quotes from multiple carriers, enabling efficient comparison shopping and market analysis. However, these car insurance calculator platforms may use simplified algorithms that don’t capture all carrier-specific discounts, underwriting nuances, or specialized programs that could significantly impact final pricing.
Independent Agent Calculator Systems: Some independent insurance agencies offer car insurance calculator tools accessing multiple carrier pricing systems while providing personalized guidance throughout the comparison process. These hybrid approaches combine multi-carrier comparison capabilities with professional expertise and ongoing service relationships.
6.3 Financial Planning Integration and Decision Support
The most valuable car insurance calculator tools integrate with broader financial planning considerations, helping users understand insurance decisions within their comprehensive financial context and long-term objectives.
Budget Planning Integration Capabilities: Advanced car insurance calculator platforms allow users to model insurance costs alongside other vehicle-related expenses—loan payments, maintenance, fuel costs, registration fees—to understand total ownership costs. This comprehensive approach supports better decision-making about vehicle purchases and coverage selections.
Risk Tolerance Assessment Integration: Premium calculator tools including risk assessment questionnaires help users align coverage selections with their financial situations and personal risk tolerance levels. These personalized recommendations ensure coverage adequacy while optimizing costs based on individual circumstances and preferences.
Insurance Program Optimization: Comprehensive car insurance calculator platforms evaluate not just premium costs but overall insurance program effectiveness, including claims handling quality, customer service ratings, and financial stability metrics. These holistic assessments help users select carriers and coverage combinations that provide optimal long-term value.
Decision Framework Development: The best car insurance calculator tools provide structured decision-making frameworks that help users prioritize different factors—cost, coverage, service quality, convenience—based on their specific needs and circumstances. These guided approaches prevent overwhelm while ensuring thorough consideration of all relevant factors.
For drivers seeking comprehensive analysis extending beyond basic premium calculations, exploring auto insurance estimate tools that incorporate multiple financial factors provides valuable insights into total insurance program optimization and strategic financial planning integration.
Conclusion: Mastering Car Insurance Calculator Strategy for Maximum Savings
Car insurance calculator mastery represents one of the most powerful tools available to modern consumers for optimizing insurance costs while ensuring adequate financial protection. Understanding how to strategically leverage these sophisticated platforms can generate substantial savings—often $400-800 annually—while improving coverage quality through informed decision-making.
Strategic Implementation Framework: ✓ Master platform selection by choosing calculators that access real-time databases and provide transparent methodologies
✓ Prepare comprehensive documentation to ensure accurate estimates and prevent underwriting surprises
✓ Utilize advanced features like scenario modeling and risk assessment to optimize coverage combinations
✓ Compare multiple platforms to identify pricing patterns and unique opportunities across different carriers
✓ Integrate calculator insights with professional guidance for comprehensive insurance program development
✓ Monitor changes regularly as personal circumstances and market conditions evolve over time
Financial Impact Potential: Strategic car insurance calculator utilization, combined with proper platform selection and advanced feature usage, typically reduces annual insurance costs by $300-750 while potentially improving protection through better coverage optimization and carrier selection processes.
Next Steps for Implementation: Begin your optimization journey by identifying 3-4 high-quality car insurance calculator platforms—including both single-carrier and multi-carrier options—to establish baseline pricing for your current situation. Document results systematically and use them as foundation data for detailed coverage consultations with insurance professionals.
Remember that car insurance calculator tools represent powerful educational and comparison resources, but they cannot replace the value of personalized guidance from experienced insurance professionals. The most effective approach combines calculator insights with expert advice to create insurance programs providing optimal protection at competitive prices.
For comprehensive guidance on optimizing your complete car insurance strategy, including understanding how calculator insights integrate with broader coverage decisions, carrier selection processes, and long-term financial planning, ensure your insurance program supports both immediate protection needs and long-term financial objectives.
Related Insurance Resources:
- How to Calculate Car Insurance Premiums – Detailed analysis of premium calculation methodologies and factors
- Factors That Affect Car Insurance Rates – Comprehensive examination of rate-influencing variables and optimization strategies
- Understanding Coverage Types – Complete guide to coverage options and protection levels
FAQ
How do you calculate insurance on a car?
Car insurance calculations involve sophisticated algorithms that analyze multiple risk factors simultaneously. Modern car insurance calculator systems process hundreds of data points through predictive modeling to determine individual premium pricing.
Primary calculation components:
Demographic factors: Age, gender, marital status, occupation
Geographic location: ZIP code-specific crime rates, accident frequency, weather patterns
Driving history: Traffic violations, accidents, claims within 3-5 years
Vehicle characteristics: Make, model, year, safety ratings, theft probability
Credit-based insurance scoring: Financial responsibility correlation (where legally permitted)
Coverage selections: Liability limits, deductibles, additional protections
The calculation process:
Base rate determination using actuarial data
Risk multiplier application based on individual factors
Discount application for qualifying criteria
State regulatory compliance adjustments
Final premium calculation with tax and fee additions
According to the document, drivers aged 16-24 file claims at rates 67% higher than experienced drivers aged 30-50, which explains why young drivers face risk multipliers of 2.5-4.0x base rates.
Is 300 dollars a month a lot for car insurance?
Yes, $300 monthly ($3,600 annually) represents significantly above-average car insurance costs. The National Association of Insurance Commissioners reports that the average American spends $1,127 annually on auto insurance, making $300 monthly about 3.2 times the national average.
Context for high premiums:
Young drivers: 18-year-old drivers average $3,608 annually (about $300 monthly)
High-risk drivers: Multiple violations or accidents can push costs this high
Expensive coverage areas: Urban ZIP codes in states like Nevada ($3,216 annually average)
Luxury/high-performance vehicles: Sports cars and expensive vehicles cost more to insure
Full coverage with low deductibles: Comprehensive protection increases costs
Potential cost reduction strategies:
Shop multiple carriers using car insurance calculator tools
Increase deductibles to lower monthly premiums
Bundle with home insurance for multi-policy discounts
Improve credit score in states allowing credit-based pricing
Take defensive driving courses for qualification discounts
The document notes that smart calculator users consistently pay 20-40% below national averages through strategic shopping.
External Resource: For personalized rate comparisons and cost reduction strategies, use Progressive’s Insurance Calculator which provides real-time quotes based on individual risk profiles.
What’s a normal monthly rate for car insurance?
Based on national data, normal monthly car insurance costs range from $75-125 for most drivers with clean records and standard coverage. The national average of $1,127 annually breaks down to approximately $94 monthly.
Monthly cost ranges by demographics:
Experienced drivers (30-50): $75-100 monthly
Young adults (25-29): $90-130 monthly
Teen drivers (16-24): $200-350+ monthly
Seniors (65+): $80-110 monthly
Geographic variations:
Rural/low-cost states: $60-90 monthly (Maine, Vermont, New Hampshire)
Urban/expensive states: $150-250+ monthly (Nevada, Louisiana, Florida)
Average-cost markets: $85-115 monthly (most of the Midwest)
Coverage level impact:
State minimums: $40-80 monthly
Full coverage: $85-140 monthly
High limits/low deductibles: $120-200+ monthly
The document emphasizes that drivers who properly utilize multiple car insurance calculator platforms typically save $300-800 annually compared to those accepting first quotes.
External Resource: The Insurance Information Institute provides comprehensive national and state-specific premium data and consumer cost analysis.
Is it normal to pay $200 for car insurance?
$200 monthly ($2,400 annually) falls above normal ranges for most drivers but can be typical in specific high-risk situations. This amount represents about 2.1 times the national average, indicating either challenging risk factors or insufficient shopping comparison.
Situations where $200 monthly might be normal:
Teen drivers: Young males especially face premiums in this range
Multiple violations: Recent accidents or traffic tickets increase costs substantially
High-risk locations: Urban areas in expensive states like California or Florida
Luxury vehicles: High-value cars with expensive repair costs
Poor credit: In states allowing credit scoring, poor credit can double premiums
Red flags suggesting overpayment:
Clean driving record with standard vehicle
Rural location in low-cost state
Good credit score and stable employment
Limited coverage selections
Optimization strategies:
Use car insurance calculator tools from multiple carriers
Consider higher deductibles to reduce monthly costs
Bundle policies for multi-line discounts
Evaluate coverage needs and eliminate unnecessary options
The document shows that MoneyGeek analysis found urban drivers face up to 214% higher premiums than rural counterparts, which could explain elevated costs.
External Resource: For comprehensive rate comparison and optimization strategies, visit The Zebra’s Car Insurance Calculator which provides detailed market analysis and cost reduction recommendations.
What is the formula for car insurance?
Car insurance calculation formulas combine base rates with multiple risk multipliers and discount factors. While specific formulas are proprietary, the general structure follows this framework:
Basic Premium Formula: Final Premium = (Base Rate × Risk Multipliers × Coverage Factors) – Applicable Discounts + Fees
Risk multiplier components:
Age factor: 0.8-4.0x based on statistical claim patterns
Location factor: 0.7-2.5x based on ZIP code risk assessment
Vehicle factor: 0.8-1.8x based on safety ratings and theft probability
Credit factor: 0.6-2.0x where legally permitted
Driving record factor: 1.0-3.0x based on violations and claims
Coverage calculation elements:
Liability limits: Higher limits increase base costs
Deductible levels: Higher deductibles reduce premiums significantly
Optional coverages: Each addition increases total premium
Discount applications:
Multi-policy bundling: 5-25% reduction
Good driver discounts: 10-23% for clean records
Safety equipment: 5-15% for anti-theft systems
Educational discounts: 5-15% for good students or defensive driving
The document notes that sophisticated algorithms access multiple databases simultaneously—MVR records, credit reports, CLUE claims history—to apply these formulas accurately.
External Resource: For detailed explanation of premium calculation methodologies and actuarial principles, visit the Casualty Actuarial Society which provides educational resources about insurance mathematics and risk assessment.
Does credit score affect car insurance?
Yes, credit scores significantly affect car insurance premiums in most states. The document reveals that drivers with poor credit pay 104% more for full coverage compared to those with excellent credit scores, according to Bankrate’s research.
Credit score impact by state:
Prohibited states: California, Hawaii, Massachusetts, Michigan, Montana, North Carolina, Pennsylvania
Restricted states: Some limitations on credit usage
Unrestricted states: Full credit-based insurance scoring permitted
Why credit affects insurance: NAIC research demonstrates that drivers with poor credit file claims 40% more frequently than those with excellent credit, creating statistical justification for pricing differences.
Credit improvement benefits:
Moving from poor to good credit may reduce premiums by $500-1,500 annually
Credit repair represents one of the most cost-effective ways to lower insurance costs
Improvements typically take 3-6 months to reflect in insurance pricing
Credit-based insurance scoring factors:
Payment history (most important factor)
Credit utilization ratios
Length of credit history
Types of credit accounts
Recent credit inquiries
The document emphasizes that credit-based insurance scores differ from regular credit scores and focus specifically on factors correlating with insurance claim patterns.
External Resource: The Consumer Financial Protection Bureau provides comprehensive information about credit scoring and its impact on various financial products, including insurance.
Who normally has the cheapest car insurance?
Several demographic and geographic groups typically qualify for the cheapest car insurance rates based on statistical risk patterns and market competition.
Demographics with lowest rates:
Experienced drivers aged 30-50: Lowest claim rates and most favorable pricing
Married drivers: Statistical evidence of safer driving patterns
Good students: Academic achievement correlates with responsible behavior
Professional occupations: Teachers, engineers, scientists often qualify for discounts
Homeowners: Property ownership indicates financial stability
Geographic advantages:
Rural residents: Lower traffic density and accident rates
Low-cost states: Maine ($1,175 annually), New Hampshire ($1,265), Vermont ($1,319)
Areas with competitive markets: Multiple insurers create pricing pressure
Vehicle-related factors:
Safe, mainstream vehicles: Good crash ratings and low theft probability
Older drivers with newer cars: Combination of experience and safety features
Low annual mileage: Less exposure equals lower premiums
Financial characteristics:
Excellent credit scores: Up to 50% savings in permissible states
Continuous coverage history: No gaps prevent penalties
Claims-free records: Long-term clean history earns substantial discounts
The document notes that smart calculator users consistently pay 20-40% below national averages through strategic optimization.
Does auto insurance increase with age?
Auto insurance costs follow a U-shaped pattern with age—starting very high for teens, dropping to lowest levels for middle-aged drivers, then increasing modestly for seniors due to different risk factors.
Age-based pricing patterns:
Ages 16-24: Highest rates due to inexperience and risk-taking behavior
Ages 25-50: Lowest rates reflecting optimal experience and responsibility
Ages 50-65: Continued low rates with potential senior discounts
Ages 65+: Slight increases due to slower reflexes and increased claim costs
Why rates change with age: CDC research shows fatal crash rates are three times higher for drivers under 20 compared to experienced adults. However, reaction time and vision changes can increase senior driver risks.
Teen vs. adult comparison:
18-year-old drivers: Average $3,608 annually
Drivers in their 50s: Average $2,008 annually
Nearly 80% difference for identical coverage
Senior driver considerations:
Some insurers offer mature driver discounts
Low-mileage discounts benefit retired drivers
Defensive driving courses can offset age-related increases
Good health can help maintain favorable rates
Optimization strategies by age:
Young drivers: Focus on good student discounts, defensive driving courses
Middle-aged drivers: Bundle policies, maintain clean records
Senior drivers: Low-mileage programs, mature driver courses
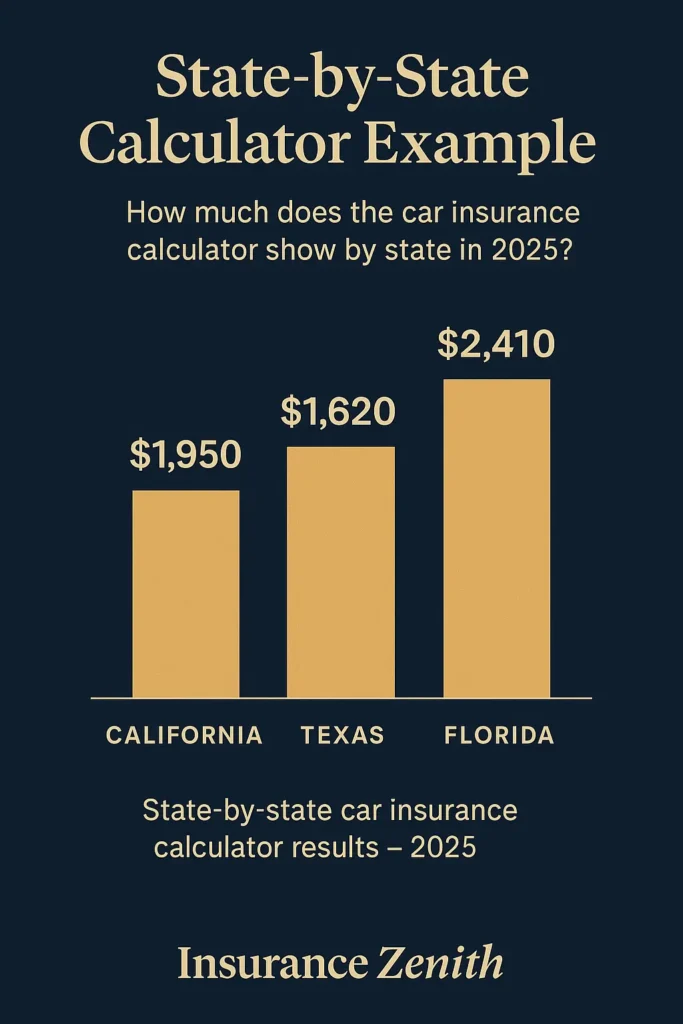
What state has the most expensive car insurance?
Nevada has the most expensive car insurance at $3,216 annually, followed by Louisiana at $2,883 and Florida at $2,694, according to the document data.
Nevada’s high costs stem from:
Urban concentration effects: Most residents in Las Vegas and Reno create traffic density
24/7 entertainment economy: Heavy traffic at all hours increases accidents
Rapid population growth: Strained infrastructure and construction zones
Tourism-related risks: Unfamiliar drivers and entertainment district hazards
Other expensive states:
Louisiana ($2,883): Severe weather, high litigation rates, many uninsured drivers
Florida ($2,694): Hurricane exposure, no-fault system, extensive fraud
Cost comparison perspective:
Most expensive (Nevada): $3,216 annually
Least expensive (Maine): $1,175 annually
Difference: Over $2,000 annually in potential geographic savings
Within-state variations: Even expensive states show dramatic regional differences. Urban ZIP codes consistently cost more due to higher theft rates, more accidents, and expensive repair facilities.
Contributing factors to high state costs:
Natural disaster exposure (hurricanes, hail, flooding)
High litigation rates and generous jury awards
Extensive insurance fraud
Dense urban populations
High uninsured motorist rates
Expensive vehicle repair costs
The document emphasizes that geographic arbitrage works both ways—relocating from expensive to cheap states saves thousands annually, while the reverse creates budget shock.